TS-8200-4500
 | |
| Product Page | |
| Documentation | |
|---|---|
| Schematic | |
| PCB Sources | |
| Temperature Sensor Datasheet |
Overview
The TS-8200 is a TS-SOCKET Baseboard that provides a test and development platform for embeddedTS' TS-4xxx products and accepts any TS-4xxx System-on-Module (SoM). The TS-8200 provides industry standard connectors for the various ports and features on many of the embeddedTS SoM products like the TS-4500, TS-4200, etc. It provides transceivers for the RS-232 ports, CAN port, and the RS-485 port, brought out to the male DB9 and .1" pitch header connections. It also has the Ethernet magnetics, RJ-45 connector, USB Host and Device connectors, Temperature Sensor, MicroSD card socket, RTC Battery (coin cell), and two LEDs. Power input requirement is regulated 5.0 to 12.0 VDC.
TS-4500
See the TS-4500 page for functionality regarding the CPU, FPGA, and OS.

|
Cavium CNS2132 250MHz ARM9 |
Getting Started
The TS-8200 board has no specific boot sequence since the processor and Linux Operating System are located on the selected TS-4000 Series System-on-Module (SoM). For the rest of the boot and setup procedure, please refer to the manual for the selected TS-4000 series SoM you are using listed here.
Before attempting to apply power to the TS-8200, perform the following steps while taking proper static discharge precautions
- Place the TS-8200 base board on a firm non-conductive surface.
- Carefully, insert the TS-4000 Series SoM by aligning and pressing evenly and firmly onto the pair of mating connectors
- Connect the console serial terminal cable
- Connect the Ethernet cable if applicable.
- Apply power
- Monitor the TS-SOCKET SBC using a terminal emulator connected to the serial console port to verify that the board is operating properly
- Connect either a regulated 5.0 to 12.0 VDC on the power input connector or the regulated 5.0 VDC via USB Device port. Please note the polarity printed on the board.
See the TS-4500 page for more details on dealing with the functionality of the System-on-Module (SoM).
Features
Push Switch
The TS-8200 contains a push switch that has multiple functions. On unit reset (or power on) the switch connects to a simple DIO input where the state of the switch may be read. The initial startup software may branch and perform any required functionality based on the switch state. By default most TS-SOCKET products will use this switch to change the console between the Debug port and the second serial port. Please refer to the manual for the selected TS-4000 series System-on-Module (SoM) that is being used listed here. The switch may also be deployed as a reset button, by setting an enable bit within the FPGA. This is the default behavior of the linuxrc on most of the TS-SOCKET products; the push button will be enabled as a reset approximately 2 seconds after a reset or power on, after it has done the change console check.
Ethernet
The TS-8200 contains a single Ethernet port interface utilizing an MMT MJKF4602 RJ-45 jack with integrated magnetics and both Link Activity and Speed LEDs. The LINK LED (right side of connector, green) is active when a valid Ethernet link is detected. This LED should be ON whenever the TS-8200 is powered and properly connected to a 10/100 BaseT Ethernet network.
MicroSD Interface
This MicroSD is on the same lines as the MicroSD on the System-on-Module. Only one can be populated at the same time.
FPGA JTAG
The JTAG header is used at the factory for programming the FPGA and CPLD. It is not available for JTAG debugging on the CPU. Using the JTAG pins to program the FPGA is not supported and not recommended.
Jumpers
| Jumper | Function |
|---|---|
| JTAG Enable | Enables writing to the FPGA. |
| Write Enable | Reserved |
| Boot SDCard | Jumper on boots to SD |
| Jumper off boots to XNAND |
Temperature Sensor
See the ts7500ctl for usage and sources for interacting with the TS-4500 temperature sensor, however this baseboard also has one that is usable through I2C.
This example shows reading the sensor:
# Only needed in debian
source /initrd/ts7500.subr
gettemp
DB9
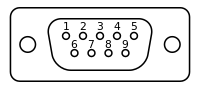
| DB9 Pin | TS-Socket Location | Name | SoM Usage |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | CN2 78 / CN2 80 | DIO_36 / DIO_37 | RS485+ on XUART0 |
| 2 | CN2 95 | DEBUG_RXD | RS232 Console RXD on ttyS0 |
| 3 | CN2 93 | DEBUG_TXD | RS232 Console TXD on ttyS0 |
| 4 | CN2 97 / CN2 99 | CAN_H | CAN0 |
| 5 | GND | Ground | N/A |
| 6 | CN2 78 / CN2 80 | DIO_36 / DIO_37 | RS485- on XUART0 |
| 7 | CN2 82 | DIO_38 | RS232 serial TXD for XUART1 |
| 8 | CN2 84 | PB7 | RS232 serial RXD for XUART1 |
| 9 | CN2 97 / CN2 99 | CAN_L | CAN0 |
USB0

This is brought out as a USB 2.0 host.
| Header PIN | TS-Socket Location | Name |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | N/A | USB_5V |
| 2 | CN2 29 | HOSTA_USB_M |
| 3 | CN2 31 | HOSTA_USB_P |
| 4 | N/A | GND |
| Note: | USB_5V can be toggled using DIO DIO_07. |
USB 1
This is a 5 pin header brought out as a USB 2.0 host.
| Header PIN | TS-Socket Location | Name |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | N/A | Frame |
| 2 | N/A | GND |
| 3 | CN2 37 | HOSTB_USB_P |
| 4 | CN2 35 | HOSTB_USB_M |
| 5 | N/A | USB_5V |
| Note: | USB_5V can be toggled using DIO DIO_07. |
USB DEV

The TS-4500 CPU supports USB Device.
| Header PIN | TS-Socket Location | Name |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | N/A | 5V |
| 2 | CN2 23 | DEV_USB_M |
| 3 | CN2 25 | DEV_USB_P |
| 4 | N/A | GND |
Revisions and Changes
TS-8200 PCB Revisions
| Revision | Changes |
|---|---|
| A |
|
| B |
|
FCC Advisory
This equipment generates, uses, and can radiate radio frequency energy and if not installed and used properly (that is, in strict accordance with the manufacturer's instructions), may cause interference to radio and television reception. It has been type tested and found to comply with the limits for a Class A digital device in accordance with the specifications in Part 15 of FCC Rules, which are designed to provide reasonable protection against such interference when operated in a commercial environment. Operation of this equipment in a residential area is likely to cause interference, in which case the owner will be required to correct the interference at his own expense.
If this equipment does cause interference, which can be determined by turning the unit on and off, the user is encouraged to try the following measures to correct the interference:
Reorient the receiving antenna. Relocate the unit with respect to the receiver. Plug the unit into a different outlet so that the unit and receiver are on different branch circuits. Ensure that mounting screws and connector attachment screws are tightly secured. Ensure that good quality, shielded, and grounded cables are used for all data communications. If necessary, the user should consult the dealer or an experienced radio/television technician for additional suggestions. The following booklets prepared by the Federal Communications Commission (FCC) may also prove helpful:
How to Identify and Resolve Radio-TV Interference Problems (Stock No. 004-000-000345-4) Interface Handbook (Stock No. 004-000-004505-7) These booklets may be purchased from the Superintendent of Documents, U.S. Government Printing Office, Washington, DC 20402.
Limited Warranty
See our Terms and Conditions for more details.