TS-8150-4712
 | |
| Product Page | |
| Product Images | |
| Specifications | |
| TS-8150 | |
|---|---|
| Schematic | |
| Mechanical Drawing | |
| TS-4712 | |
| Schematic | |
| Mechanical Drawing | |
| FTP Path | |
| Processor | |
| Marvell PXA166 or PXA168 | |
| 800MHz or 1066MHz ARMv5TE Mohawk (ARM9 compatible) | |
| CPU Series Website | |
| PXA16X Software Guide |
Overview
The TS-8150 is a low cost TS-Socket Baseboard in the same form factor as the TS-7260, TS-7800, and TS-8160. This board provides a second Ethernet using the port provided by the System-on-Module's Ethernet switch.
The TS-4712 is a TS-Socket System-on-Module (SoM) based on the TS-4700 with a revised FPGA to CPU interface, a faster CPU, more memory, dual Ethernet, dual SD cards for DoubleStore support, and a significantly faster boot time.
Getting Started
A Linux workstation is recommended and assumed for development using this documentation. For users in Windows or OSX, we recommend virtualizing Linux. Most of our platforms run Debian, which is recommended for ease of use if there is no personal distribution preference.
Virtualization
Suggested Linux Distributions
Development using a Windows or OSX system may be possible but is not supported. Development will include accessing drives formatted for Linux and often Linux-based tools.
Booting up the board
| WARNING: | Be sure to take appropriate Electrostatic Discharge (ESD) precautions. Disconnect the power source before moving, cabling, or performing any set up procedures. Inappropriate handling may cause damage to the board. |
This board accepts 5-28VDC input connected to the two terminal blocks.
 |
While operating the board will typically idle at around 340mA@5V, but this can very slightly based on your application. For example, every USB device can consume up to 500mA@5V. The ethernet interface can draw around 50mA while the interface is up. Every DIO pin can source up to 12mA from the FPGA. A Sandisk SD card can draw 65mA@3.3V during a write. A typical power supply for just the TS-8100-4700 will allow around 10W, but a larger power supply may be needed depending on your peripherals.
Once you have applied power to your baseboard you should look for console output. Creating this connection is described more in the next chapter, but the first output is from the bootrom:
>> TS-BOOTROM - built Dec 21 2011 10:05:44 >> Copyright (c) 2011, Technologic Systems >> Booting from microSD card ... . . .
The 3 dots after indicate steps of the booting procedure. The first dot means the MBR was copied into memory and executed. The next two dots indicate that the MBR executed and the kernel and initrd were found and copied to memory.
Get a Console
Option 1: Telnet
If your system is configured with zeroconf support (Avahi, Bonjour, etc) you can simply connect to the TS-4710 with:
telnet ts4710-<last 6 characters of the MAC address>.local
# You will need to use your TS-4710 MAC address, but
# for example if you mac is 00:d0:69:01:02:03
telnet ts4710-010203.local
When the board first powers up it has two network interfaces. The first interface eth0 is configured to use IPv4LL, and eth0:0 is configured to use DHCP. The board broadcasts using multicast DNS advertising the _telnet._tcp service. You can use this to query all of the available TS-4710s on the network.
From Linux you can use the avahi commands to query for all telnet devices with:
avahi-browse _telnet._tcp
Which would return:
+ eth0 IPv4 TS-4710 console [4f47a5] Telnet Remote Terminal local + eth0 IPv4 TS-4710 console [4f471a] Telnet Remote Terminal local
This will show you the mac address you can use to resolve the board. In this case you can connect to either ts4710-4f47a5 or ts4710-4f47a5.
From Windows you can use Bonjour Print Services to get the dns-sd command. OSX also comes preinstalled with the same command. Once this is installed you can run:
dns-sd -B _telnet._tcp
Which will return:
Browsing for _telnet._tcp Timestamp A/R Flags if Domain Service Type Instance Name 10:27:57.078 Add 3 2 local. _telnet._tcp. TS-4710 console [4f47a5] 10:27:57.423 Add 3 2 local. _telnet._tcp. TS-4710 console [4f47a5]
This will show you the mac address you can use to resolve the board. In this case you can connect to either ts4710-4f47a5.local or ts4710-4f47a5.local.
Option 2: Serial Console
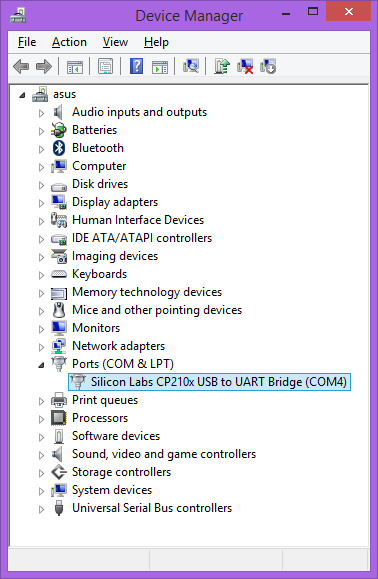
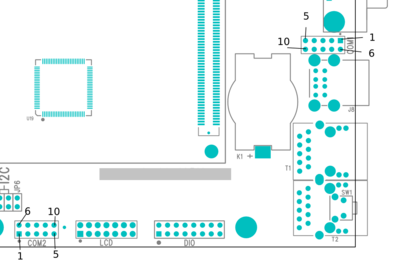
The TS-8150 console is an RS232 UART at 115200 baud, 8n1 (8 data bits 1 stop bit), and no flow control. You will need a NULL MODEM cable. On the TS-8150 you need to set the "Console Enable" jumper as pictured:

|
Note: TS-8100 pictured above, your product may vary slightly in placement and nomenclature.
This will bring the console UART to both the DB9 Port, and the COM1 Header.
| Note: | If DIO_9 is held low during boot until the red LED comes on (around 5 seconds), console will be redirected to XUART 0. On the TS-8150 DIO9 is installed as a push switch if the second ethernet is not installed. |
Console from Linux
There are many serial terminal applications for Linux, three common used applications are picocom, screen, and minicom. These examples demonstrate all three applications and assume that the serial device is "/dev/ttyUSB0" which is common for USB adapters. Be sure to replace the serial device string with that of the device on your workstation.
picocom is a very small and simple client.
sudo picocom -b 115200 /dev/ttyUSB0
screen is a terminal multiplexer which happens to have serial support.
sudo screen /dev/ttyUSB0 115200
Or a very commonly used client is minicom which is quite powerful but requires some setup:
sudo minicom -s
- Navigate to 'serial port setup'
- Type "a" and change location of serial device to "/dev/ttyUSB0" then hit "enter"
- If needed, modify the settings to match this and hit "esc" when done:
E - Bps/Par/Bits : 115200 8N1
F - Hardware Flow Control : No
G - Software Flow Control : No
- Navigate to 'Save setup as dfl', hit "enter", and then "esc"
Console from Windows
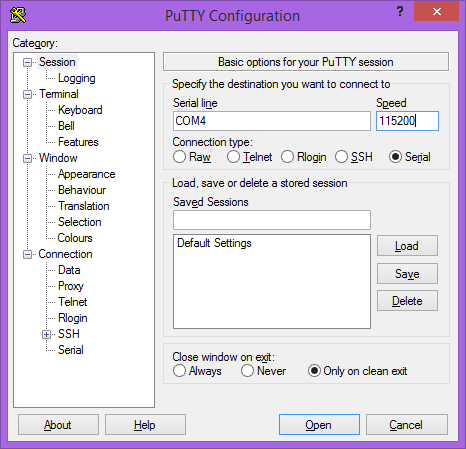
Putty is a small simple client available for download here. Open up Device Manager to determine your console port. See the putty configuration image for more details.
Initrd / Busybox
When the board first boots up you should have a console such as:
>> TS-BOOTROM - built Mar 14 2013 15:01:50 >> Copyright (c) 2012, Technologic Systems . . Uncompressing Linux... done, booting the kernel. Booted in 0.90s Initramfs Web Interface: http://ts47XX-112233.local
This is a minimalistic initial ram filesystem that includes our specific utilities for the board, and is then used to bootstrap the Linux root. The initramfs is built into the kernel image so it cannot be modified without rebuilding the kernel, but it does read several bits from nonvolatile memory for common configuration options we call soft jumpers. Note: Soft jumper settings are not stored on the SD media, so re-flashing your SD card will not reset the soft jumpers. This action can only be taken from within the OS.
| WARNING: | Setting soft jumper 1 will boot the system straight to Debian, leaving the serial port as the only default access method. Ensure that alternate access methods (telnet, SSH, etc.) are set up and working in Debian if the serial port is not a viable access method before this jumper is set. If a lockout situation does occur, please contact us at support@embeddedTS.com |
| Jumper | Function |
|---|---|
| 1 | Boot automatically to Debian [1] |
| 2 | Reserved |
| 3 | Reserved |
| 4 | Reserved |
| 5 | Reserved |
| 6 | Reserved |
| 7 | Skip most of the init. [2] |
| 8 | Skip full DRAM test on startup [3] |
- ↑ Initramfs boot is default. Be sure to configure Debian before setting this jumper if serial port access is not possible, see "Warning" above.
- ↑ This option skips a significant amount of setup and will boot to a single SD card as fast as possible with no initialization. This mode will still execute /mnt/root/ts/init if it exists, or boot to Debian if jp1 is set. Note that this will not initialize any networking in the initramfs, leaving the serial port as the only access method. If booting to Debian, see "Warning" above.
- ↑ The DRAM test can be used to verify the RAM, but adds approximately 20 seconds to the boot time. This should normally only be enabled when diagnosing problems.
There are 2 ways to manipulate soft jumpers on the board. The web interface at
"http://ts<model>-<last 6 chars of the MAC>.local"
has a list of checkboxes that will immediately change the values. You can also use tshwctl:
# Boot automatically to Debian:
tshwctl --setjp=1
# Or revert to the initramfs:
tshwctl --removejp=1
The Debian boot can also be inhibited by creating a file in /ts/fastboot in the Debian root. While this file exists the board will stop booting at the initramfs. If you do not have a serial console, make sure you first configure Debian's network settings first before booting directly to Debian. Once JP1 is enabled, the initramfs does not run ifplugd/udhcpc to configure the network.
Most development should be done in Debian, however many applications are capable of running from the initramfs. Utilities from Debian can be accessed under /mnt/root as read only, but for Debian services, or using apt-get a full boot into Debian should be performed. The initramfs itself cannot be easily modified, and it is not recommended to do so. The initramfs however has several hooks for applications to manipulate it's behavior.
/mnt/root/ts/init
For headless applications you can create a bash script with any initialization you require in /ts/init. This does not use the same $PATH as Debian, so you should enter the full path to any applications you intend to run from this environment. The init file does not exist by default and must be created.:
#!/bin/sh
/path/to/your/application &
Remember to set it executable!
chmod a+x /ts/init
/mnt/root/ts/initramfs-xinit
Graphical applications run in the initramfs should use /ts/initramfs-xinit. Users booting to Debian should use /usr/bin/default-x-session. The xinit file is used to start up a window manager and any applications. The default initramfs-xinit starts a webbrowser viewing localhost:
#!/bin/sh
# Causes .Xauthority and other temp files to be written to /root/ rather than default /
export HOME=/root/
# Disables icewm toolbars
export ICEWM_PRIVCFG=/mnt/root/root/.icewm/
# minimalistic window manager
icewm-lite &
# this loop verifies the window manager has successfully started
while ! xprop -root | grep -q _NET_SUPPORTING_WM_CHECK
do
sleep 0.1
done
# This launches the fullscreen browser. If the xinit script ever closes, x11 will close. This is why the last
# command is the target application which is started with "exec" so it will replace the xinit process id.
exec /usr/bin/fullscreen-webkit http://localhost
/mnt/root/ts/config
This config file can be used to alter many details of the initramfs boot procedure.
## This file is included by the early init system to set various bootup settings. ## if $jp7 is enabled none of these settings will be used. ## Used to control whether the FPGA is reloaded through software. ## 1 to enable reloading (default) ## 0 to disable reloading #CFG_FPGARELOAD="0" ## By default dns-sd is started which advertises the ts<model>-<last 6 of mac> ## telnet and http services using zeroconf. ## 1 to enable dns-sd (default) ## 0 to disable dns-sd #CFG_DNSSD_EN="0" ## This is used to discover hosts and advertise this host over multicast DNS. ## 1 to enable mdns (default) ## 0 to disable mdns #CFG_MDNS_EN="0" ## ifplugd is started in the initramfs to start udhcpc, and receive an ipv4ll ## address. ## 1 to enable ifplugd (default) ## 0 to disable ifplugd #CFG_IFPLUGD_EN="0" ## By default telnet is started on port 2323. ## 1 to enable telnet (default) ## 0 to disable telnet ##CFG_TELNET_EN="0" ## The busybox webserver is used to display a diagnostic web interface that can ## be used for development tasks such as rewriting the SD or uploading new ## software ## 1 to enable (default) ## 0 to disable ##CFG_HTTPD_EN="0" ## This eanbles a reset switch on DIO 29 (TS-7700), or DIO 9 on all of the ## boards (except TS-7250-V2). Pull low to reset the board immediately. ## 1 to enable the reset sw (default) ## 0 to disable #CFG_RESETSW_EN="0" ## The console is forwarded through xuartctl which makes the cpu console available ## over telnet or serial console. ## 1 to enable network console (default) ## 0 to disable network console #CFG_NETCONS_EN="0" ## By default Alsa will put the SGTL5000 chip into standby after 5 seconds of ## inactivity. This is desirable in that it results in lower power consumption, ## but it can result in an audible popping noise. This setting prevents ## standby so the pop is never heard. ## 1 to disable standby ## 0 to enable standby (default) #CFG_SGTLNOSTBY="1" ## xuartctl is used to access the FPGA uarts. By default it is configured to ## be IRQ driven which is optimized for best latency, but at the cost of ## additional CPU time. You can reduce this by specifying a polling rate. ## The xuartctl process also binds to all network interfaces which can provide a ## simple network API to access serial ports remotely. You can restrict this to ## the local network with the bind option. ## Configure XUART polling 100hz ## Default is IRQ driven CFG_XUARGS="--irq=100hz" ## Configure xuartctl to bind on localhost ## Default binds on all interfaces #CFG_XUARGS="--bind 127.0.0.1 --irq=100hz" ## For a full list of arguments, see the xuartctl documentation here: ## http://docs.embeddedts.com/wiki/Xuartctl#Usage ## By default the system will probe for up to 10s on USB for a mass storage device ## and mount the first partition. If there is an executable /tsinit script in the ## root this will be executed. This is intended for production or updates. ## 2 to enable USB init always (adds 10s or $CFG_USBTIME to startup) ## 1 to enable USB init when jp1=0 (default) ## 0 to disable USB init always #CFG_USBINIT="2" ## The USB init script by default blocks for 10s to detect a thumb drive that ## contains the tsinit script. Most flash media based drives can be detected ## in 3s or less. Some spinning media drives can take 10s, or potentially longer. ## This options is the number of seconds to wait before giving up on the ## mass storage device. #CFG_USBTIME="3" ### TS-8700 ## Using the TS-8700 baseboard the board will by default initialze all of the ## ethernet ports as individual vlan ports, eg eth0.1, eth0.2, eth0,3, and eth0.4 ## The alterantive option sets Port A to eth0.1, and Ports B-D to eth0.2, or ## you can configure all ethernet ports as a single eth0 port. ## See http://docs.embeddedts.com/wiki/TS-8700 for more information ## 2 disables any vlan and passes through all interfaces to eth0 ## 1 enables "WLAN" mode setting "A" as eth0.1, and all others as eth0.2 ## 0 enables "VLAN" mode for 4 individual ports (default) #CFG_4ETH="1" ### TS-4712 / TS-4720 ## These boards include an onboard switch with 2 external ports. By default ## the switch will detect if it is on a known baseboard that supports the second ## ethernet switch port, and set up VLAN rules to define eth0.1 and eth0.2. The ## other option is to configure the switch to pass through the packets to eth0 ## regarless of port. ## 2 Disable VLAN and pass through to eth0 ## 1 Enable VLAN on all baseboards ## 0 Enable VLAN on supported baseboards (Default) #CFG_2ETH="1"
Debian Configuration
For development, it is recommended to work directly in Debian on the SD card. Debian provides many more packages and a much more familiar environment for users already versed in Debian. Through Debian it is possible to configure the network, use the 'apt-get' suite to manage packages, and perform other configuration tasks. Out of the box the Debian distribution does not have any default username/password set. The account "root" is set up with no password configured. It is possible to log in via the serial console without a password but many services such as ssh will require a password set or will not allow root login at all. It is advised to set a root password and create a user account when the unit is first booted.
| Note: | Setting up a password for root is only feasible on the uSD image. |
It is also possible to cross compile applications. Using a Debian host system will allow for installing a cross compiler to build applications. The advantage of using a Debian host system comes from compiling against libraries. Debian cross platform support allows one to install the necessary development libraries on the host, building the application on the host, and simply installing the runtime libraries on the target device. The library versions will be the same and completely compatible with each other. See the respective Debian cross compiling section for more information.
Configuring the Network
This board includes a Marvell switch chip which allows 2 separate networks using the same network interface. See the Ethernet port section for more information on the switch settings. When the switch is configured for 2 separate networks (as it is by default), the eth0 interface should not be directly configured. The switch will provide the eth0.1 and eth0.2 interfaces which can be configured. If the switch is configured to pass through, then the eth0 interface should be used as normal.
The board is initially configured to boot to the initramfs. While in this state ifplugd will automatically assign an IP address, and even if you type "exit" to boot to Debian it will retain the address it was assigned. If you need to boot to the full Debian, networking should first be set up in the /etc/network/interfaces file. As an example, to get dhcp from eth0.1: Open /etc/network/interfaces
# We always want the loopback interface.
auto lo
iface lo inet loopback
auto eth0.1
iface eth0.1 inet dhcp
Once this file is set up, either reboot or "/etc/init.d/networking restart" for this to take effect.
From almost any Linux system you can use "ip" or the ifconfig/route commands to manually set up the network. To configure the network interface manually you can use the same set of commands in the initramfs or Debian.
# NOTE: These are generic examples. Be sure to read the entire networking section before trying any of these.
# Bring up the CPU network interface (for systems with only one Ethernet)
ifconfig eth0 up
# Or if you're on a baseboard with a second ethernet port, you can use that as:
ifconfig eth1 up
# Or if you're on a TS-7250-V2...
ifconfig eth0.1 up
ifconfig eth0.2 up
# Set an ip address (assumes 255.255.255.0 subnet mask)
ifconfig eth0 192.168.0.50
# Set a specific subnet
ifconfig eth0 192.168.0.50 netmask 255.255.0.0
# Configure your route. This is the server that provides your internet connection.
route add default gw 192.168.0.1
# Edit /etc/resolv.conf for your DNS server
echo "nameserver 192.168.0.1" > /etc/resolv.conf
Most commonly networks will offer DHCP which can be set up with one command:
Configure DHCP in Debian:
# To setup the default CPU ethernet port
dhclient eth0
# Or if you're on a baseboard with a second ethernet port, you can use that as:
dhclient eth1
# You can configure all ethernet ports for a dhcp response with
dhclient
Configure DHCP in the initramfs:
udhcpc -i eth0
# Or if you're on a baseboard with a second ethernet port, you can use that as:
udhcpc -i eth1
To make your network settings take effect on startup in Debian, edit /etc/network/interfaces:
# Used by ifup(8) and ifdown(8). See the interfaces(5) manpage or
# /usr/share/doc/ifupdown/examples for more information.
# We always want the loopback interface.
#
auto lo
iface lo inet loopback
auto eth0
iface eth0 inet static
address 192.168.0.50
netmask 255.255.255.0
gateway 192.168.0.1
auto eth1
iface eth1 inet dhcp
| Note: | During Debian's startup it will assign the interfaces eth0 and eth1 to the detected mac addresses in /etc/udev/rules.d/70-persistent-net.rules. If the system is imaged while this file exists it will assign the new interfaces as eth1 and eth2. This file is generated automatically on startup, and should be removed before your first software image is created. The initrd network configuration does not use this file. |
| Note: | The /etc/resolv.conf file is linked to /dev/resolv.conf on purpose so both Debian and the Initramfs can use the same settings file. If configuring a static IP, replace the settings in this file with the appropriate settings for the target network. If configuring Debian to use DHCP, the file will be automatically overridden by the DHCP client, and no action is necessary. |
In this example eth0 is a static configuration and eth1 receives its configuration from the DHCP server. For more information on network configuration in Debian see their documentation here.
WIFI Client
This board optionally supports 802.11 through the WIFI-N-USB-2 module using the ath9k_htc driver.
Scan for a network
ifconfig wlan0 up
# Scan for available networks
iwlist wlan0 scan
In this case I'm connecting to "default" which is an open network:
Cell 03 - Address: c0:ff:ee:c0:ff:ee
Mode:Managed
ESSID:"default"
Channel:2
Encryption key:off
Bit Rates:9 Mb/s
To connect to this open network:
iwconfig wlan0 essid "default"
You can use the iwconfig command to determine if you have authenticated to an access point. Before connecting it will show something similar to this:
# iwconfig wlan0
wlan0 IEEE 802.11bgn ESSID:"default"
Mode:Managed Frequency:2.417 GHz Access Point: c0:ff:ee:c0:ff:ee
Bit Rate=1 Mb/s Tx-Power=20 dBm
Retry long limit:7 RTS thr:off Fragment thr:off
Encryption key:off
Power Management:off
Link Quality=70/70 Signal level=-34 dBm
Rx invalid nwid:0 Rx invalid crypt:0 Rx invalid frag:0
Tx excessive retries:0 Invalid misc:0 Missed beacon:0
If you are connecting using WEP, you will need to define a network key:
iwconfig wlan0 essid "default" key "yourpassword"
If you are connecting to WPA you will need to use wpa_passphrase and wpa_supplicant:
wpa_passphrase the_essid the_password > /etc/wpa_supplicant.conf
Now that you have the configuration file, you will need to start the wpa_supplicant daemon:
wpa_supplicant -Dwext -iwlan0 -c/etc/wpa_supplicant.conf -B
Now you are connected to the network, but this would be close to the equivalent of connecting a network cable. To connect to the internet or talk to your internal network you will need to configure the interface. See the #Configuring the Network for more information, but commonly you can just run:
dhclient wlan0
| Note: | Some older images did not include the "crda" and "iw" packages required to make a wireless connection. If you cannot get an ip address you may want to connect over ethernet and install these packages with "apt-get install crda iw -y". |
Host a WIFI Access Point
The software image includes a build of compat-drivers from 3.8 so a large amount of wireless devices are supported. Some devices support AP/Master mode which can be used to host an access point. The WIFI-N-USB-2 module we provide also supports this mode.
First install hostapd to manage the access point:
apt-get update && apt-get install hostapd -y
Edit /etc/hostapd/hostapd.conf to include:
interface=wlan0 driver=nl80211 ssid=YourAPName channel=1
| Note: | Refer to the kernel's hostapd documentation for more wireless configuration options. |
To start the access point launch hostapd:
hostapd /etc/hostapd/hostapd.conf &
This will create a valid wireless access point, however many devices will not be able to connect without either a static connection, or a DHCP server. Refer to Debian's documentation for more details on DHCP configuration.
Installing New Software
Debian provides the apt-get system which manages pre-built applications. Before packages can be installed, the list of package versions and locations needs to be updated. This assumes the device has a valid network connection to the internet.
Debian Wheezy has been moved to archive status, this requires an update of /etc/apt/sources.list to contain only the following lines:
deb http://archive.debian.org/debian wheezy main non-free deb-src http://archive.debian.org/debian wheezy main non-free
apt-get update
apt-get install --allow-unauthenticated debian-archive-keyring
apt-get update
For example, lets say you wanted to install openjdk for Java support. You can use the apt-cache command to search the local cache of Debian's packages.
<user>@<hostname>:~# apt-cache search openjdk icedtea-6-jre-cacao - Alternative JVM for OpenJDK, using Cacao icedtea6-plugin - web browser plugin based on OpenJDK and IcedTea to execute Java applets openjdk-6-dbg - Java runtime based on OpenJDK (debugging symbols) openjdk-6-demo - Java runtime based on OpenJDK (demos and examples) openjdk-6-doc - OpenJDK Development Kit (JDK) documentation openjdk-6-jdk - OpenJDK Development Kit (JDK) openjdk-6-jre-headless - OpenJDK Java runtime, using Hotspot Zero (headless) openjdk-6-jre-lib - OpenJDK Java runtime (architecture independent libraries) openjdk-6-jre-zero - Alternative JVM for OpenJDK, using Zero/Shark openjdk-6-jre - OpenJDK Java runtime, using Hotspot Zero openjdk-6-source - OpenJDK Development Kit (JDK) source files openoffice.org - office productivity suite freemind - Java Program for creating and viewing Mindmaps default-jdk-doc - Standard Java or Java compatible Development Kit (documentation) default-jdk - Standard Java or Java compatible Development Kit default-jre-headless - Standard Java or Java compatible Runtime (headless) default-jre - Standard Java or Java compatible Runtime
In this case you will likely want openjdk-6-jre to provide a runtime environment, and possibly openjdk-6-jdk to provide a development environment. You can often find the names of packages from Debian's wiki or from just searching on google as well.
Once you have the package name you can use apt-get to install the package and any dependencies. This assumes you have a network connection to the internet.
apt-get install openjdk-6-jre
# You can also chain packages to be installed
apt-get install openjdk-6-jre nano vim mplayer
For more information on using apt-get refer to Debian's documentation here.
Setting up SSH
On our boards we include the Debian package for openssh-server, but we remove the automatically generated keys for security reasons. To regenerate these keys:
dpkg-reconfigure openssh-server
Make sure your board is configured properly on the network, and set a password for your remote user. SSH will not allow remote connections without a password or a shared key.
| Note: | Setting up a password for root is only feasible on the uSD image. |
passwd root
You should now be able to connect from a remote Linux or OSX system using "ssh" or from Windows using a client such as putty.
| Note: | If your intended application does not have a DNS source on the target network, it can save login time to add "UseDNS no" in /etc/ssh/sshd_config. |
Starting Automatically
From Debian the most straightforward way to add your application to startup is to create a startup script. This is an example simple startup script that will toggle the red led on during startup, and off during shutdown. In this case I'll name the file customstartup, but you can replace this with your application name as well.
Edit the file /etc/init.d/customstartup to contain this:
#! /bin/sh
# /etc/init.d/customstartup
case "$1" in
start)
/path/to/your/application
## If you are launching a daemon or other long running processes
## this should be started with
# nohup /usr/local/bin/yourdaemon &
;;
stop)
# if you have anything that needs to run on shutdown
/path/to/your/shutdown/scripts
;;
*)
echo "Usage: customstartup start|stop" >&2
exit 3
;;
esac
exit 0
| Note: | The $PATH variable is not set up by default in init scripts so this will either need to be done manually or the full path to your application must be included. |
To make this run during startup and shutdown:
update-rc.d customstartup defaults
To manually start and stop the script:
/etc/init.d/customstartup start
/etc/init.d/customstartup stop
While this is useful for headless applications, if you are using X11 you should modify "/usr/bin/default-x-session":
#!/bin/sh
export HOME=/root/
export ICEWM_PRIVCFG=/mnt/root/root/.icewm/
icewm-lite &
while ! xprop -root | grep -q _NET_SUPPORTING_WM_CHECK
do
sleep 0.1
done
exec /usr/bin/fullscreen-webkit http://127.0.0.1
Replace fullscreen-webkit with your own graphical application.
Backup / Restore
While all of our products ship with images pre-loaded in to any supplied media, there are many situations where new images may need to be written. NOTE: If you are using a Windows workstation there is no support for writing directly to block devices. However, as long as one of your booting methods still can boot a kernel and the initrd you can rewrite everything by using a usb drive. This is also a good way to image or re-image many stock boards when moving your product into production. You can find more information about this method with an example script on the USB-Blaster page linked here.
You can alternately use more direct methods of writing either SD or eMMC boot images, these methods (detailed below) are a good means of returning an R&D device to a known-good working software state, with the shipping images linked in their applicable section below.
| Note: | Note that the MBR installed by default on this board contains a 446 byte bootloader program that loads the initial power-on kernel and initrd from the first and second partitions. Replacing it with an MBR found on a PC would not work as a PC MBR contains an x86 code bootup program. |
MicroSD Card
| WARNING: | While tools exist for writing image from Windows or other operating systems, we do not support their use. If they are not careful to make sure the OS has not mounted the FS, or existing drivers have ceased any access to the card, they may end up with corruption that is not immediately apparent upon using the card. This may present as sublte corruption, or a card that does not boot at all. We do not encourage use of any other process other than what is described in this section. |

|
Click to download the latest 4GB SD card image. |
Using onboard web interface
The initramfs contains a #Web interface that can be used to backup/restore the software image. From the main page, you can download a complete backup containing the MBR, Kernel, initramfs, and Debian filesystem by clicking "backup.dd". You can click "Choose File" and browse to a previous backup.dd, or the link above to rewrite the SD card.
Using another Linux workstation
If you do not have an SD card that can boot to the initramfs, you can download the sd card image and rewrite this from a Linux workstation. A USB MicroSD adapter can be used to access the card. First, you must find out which /dev/ device corresponds with your USB reader/writer.
Step 1 Option 1 (lsblk)
Newer distributions include a utility called "lsblk" which allows simple identification of the intended card:
lsblk
NAME MAJ:MIN RM SIZE RO TYPE MOUNTPOINT sda 8:0 0 400G 0 disk ├─sda1 8:1 0 398G 0 part / ├─sda2 8:2 0 1K 0 part └─sda5 8:5 0 2G 0 part [SWAP] sr0 11:0 1 1024M 0 rom sdc 8:32 1 3.9G 0 disk ├─sdc1 8:33 1 7.9M 0 part ├─sdc2 8:34 1 2M 0 part ├─sdc3 8:35 1 2M 0 part └─sdc4 8:36 1 2.8G 0 part
In this case my SD card is 4GB, so sdc is the target device.
Step 1 Option 2 (dmesg)
After plugging in the device, you can use dmesg to list
scsi 9:0:0:0: Direct-Access Generic Storage Device 0.00 PQ: 0 ANSI: 2 sd 9:0:0:0: Attached scsi generic sg2 type 0 sd 9:0:0:0: [sdb] 7744512 512-byte logical blocks: (3.96 GB/3.69 GiB)
In this case, sdc is shown as a 3.96GB card.
Step 2
Once you have the target /dev/ device you can use "dd" to backup/restore the card. To restore the board to stock, or rewrite to the latest SD image:
wget https://files.embeddedTS.com/ts-socket-macrocontrollers/ts-4710-linux/binaries/ts-images/4gbsd-471x-latest.dd.bz2
bzip2 -d 4gbsd-471x-latest.dd.bz2
# Specify your block device instead of /dev/sdc
# Note that this does not include a partition, so use /dev/sdc instead of
# using /dev/sdc1
dd if=4gbsd-471x-latest.dd conv=fsync bs=4M of=/dev/sdc
To take a backup of your entire SD card, you can switch the input file and the output file:
dd if=/dev/sdc conv=fsync bs=4M of=backup.dd
Software Development
Most of our examples are going to be in C, but Debian will include support for many more programming languages. Including (but not limited to) C++, PERL, PHP, SH, Java, BASIC, TCL, and Python. Most of the functionality from our software examples can be done from using system calls to run our userspace utilities. For higher performance, you will need to either use C/C++ or find functionally equivalent ways to perform the same actions as our examples. Our userspace applications are all designed to go through a TCP interface. By looking at the source for these applications, you can learn our protocol for communicating with the hardware interfaces in any language.
The most common method of development is directly on the SBC. Since debian has space available on the SD card, we include the build-essentials package which comes with everything you need to do C/C++ development on the board.
Editors
Vim is a very common editor to use in Linux. While it isn't the most intuitive at a first glance, you can run 'vimtutor' to get a ~30 minute instruction on how to use this editor. Once you get past the initial learning curve it can make you very productive. You can find the vim documentation here.
Emacs is another very common editor. Similar to vim, it is difficult to learn but rewarding in productivity. You can find documentation on emacs here.
Nano while not as commonly used for development is the easiest. It doesn't have as many features to assist in code development, but is much simpler to begin using right away. If you've used 'edit' on Windows/DOS, this will be very familiar. You can find nano documentation here.
Compilers
We only recommend the gnu compiler collection. There are many other commercial compilers which can also be used, but will not be supported by us. You can install gcc on most boards in Debian by simply running 'apt-get update && apt-get install build-essential'. This will include everything needed for standard development in c/c++.
You can find the gcc documentation here. You can find a simple hello world tutorial for c++ with gcc here.
Build tools
When developing your application typing out the compiler commands with all of your arguments would take forever. The most common way to handle these build systems is using a make file. This lets you define your project sources, libraries, linking, and desired targets. You can read more about makefiles here.
If you are building an application intended to be more portable than on this one system, you can also look into the automake tools which are intended to help make that easier. You can find an introduction to the autotools here.
Cmake is another alternative which generates a makefile. This is generally simpler than using automake, but is not as mature as the automake tools. You can find a tutorial here.
Debuggers
Linux has a few tools which are very helpful for debugging code. The first of which is gdb (part of the gnu compiler collection). This lets you run your code with breakpoints, get backgraces, step forward or backward, and pick apart memory while your application executes. You can find documentation on gdb here.
Strace will allow you to watch how your application interacts with the running kernel which can be useful for diagnostics. You can find the manual page here.
Ltrace will do the same thing with any generic library. You can find the manual page here.
Accessing Hardware Registers
The standard assumption in Linux is that kernel drivers are required in order to control hardware. However, it is also possible to talk to hardware devices from user space. In doing so, one does not have to be aware of the Linux kernel development process. This is the recommended way of accessing hardware on a TS-SOCKET system. The special /dev/mem device implements a way to access the physical memory from the protected user space, allowing reading and writing to any specific memory register. Applications may be allowed temporary access through memory space windows granted by the mmap() system call applied to the /dev/mem device node.
The following C code is provided as an example of how to set up user space access to the SYSCON registers at base address 0x80004000:
#include <sys/mman.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/stat.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
#include <assert.h>
static volatile unsigned short *syscon;
static unsigned short peek16(unsigned int adr) {
return syscon[adr / 2];
}
static void poke16(unsigned int adr, unsigned short val) {
syscon[adr / 2] = val;
}
int main(void) {
int devmem = open("/dev/mem", O_RDWR|O_SYNC);
assert(devmem != -1);
syscon = (unsigned short *) mmap(0, 4096,
PROT_READ | PROT_WRITE, MAP_SHARED, devmem, 0x80004000);
poke16(0x6, 0x3); // disable watchdog
poke16(0x12, peek16(0x12) | 0x1800); // turn on both LEDs
return 0;
}
Important Notes about the preceding example:
- The peek16 and poke16 wrapper functions make the code more readable due to how pointer arithmetic/array indexing works in C, since the same offsets from the register map appear in the code.
- Make sure to open using O_SYNC, otherwise you may get a cachable MMU mapping which, unless you know what you're doing, probably is not what you want when dealing with hardware registers.
- mmap() must be called only on pagesize (4096 byte) boundaries and size must at least have pagesize granularity.
- Only the root user can open '/dev/mem'. For testing, this just means the tester needs to be root, which is normal in embedded Linux. For deployment in the field under Debian, this can be an issue because the init process does not have root privileges. To get around this, make sure the binary is owned by root and has the setuid bit set. The command 'chmod +s mydriver' will set the setuid flag.
- The pointers into memory space should have the same bit width as the registers they are accessing. In the example above, the TS-4710 FPGA registers are 16 bits wide, so an unsigned short pointer is used. With very few exceptions, FPGA registers on TS-SOCKET macrocontrollers will be 16 bits wide and CPU registers will be 32 bits wide. Unsigned int, unsigned short, and unsigned char pointers should be used for 32, 16, and 8 bit registers, respectively.
- When compiling ARM code that emits 16 bit or 8 bit hardware register accesses, it is important to add the compiler switch -mcpu=arm9. Otherwise the wrong opcodes may be emitted by the compiler and unexpected behavior will occur.
- Pointers into memory space must be declared as volatile.
Cross Compiling
While you can develop entirely on the board itself, if you prefer to develop from another x86 compatible Linux system we have a cross compiler available. For this board you will want to use this toolchain. To compile your application, you only need to use the version of GCC in the cross toolchain instead of the version supplied with your distribution. The resulting binary will be for ARM.
[user@localhost]$ /opt/arm-2008q3/bin/arm-none-linux-gnueabi-gcc hello.c -o hello
[user@localhost]$ file hello
hello: ELF 32-bit LSB executable, ARM, version 1 (SYSV), dynamically linked (uses shared libs), for GNU/Linux 2.6.14, not stripped
This is one of the simplest examples. If you want to work with a project, you will typically create a makefile. You can read more about makefiles here. Another common requirement is linking to third party libraries provided by Debian on the board. There is no exact set of steps you can take for every project, but the process will be very much the same. Find the headers, and the libraries. Sometimes you have to also copy over their binaries. In this example, I will link to sqlite from Debian (which will also work in the Ubuntu image).
Install the sqlite library and header on the board:
apt-get update && apt-get install -y libsqlite3-0 libsqlite-dev
This will fetch the binaries from the internet and install them. You can list the installed files with dpkg:
dpkg -L libsqlite3-0 libsqlite3-dev
The interesting files from this output will be the .so files, and the .h files. In this case you will need to copy these files to your project directory.
I have a sample example with libsqlite3 below. This is not intended to provide any functionality, but just call functions provided by sqlite.
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include "sqlite3.h"
int main(int argc, char **argv)
{
sqlite3 *db;
char *zErrMsg = 0;
int rc;
printf("opening test.db\n");
rc = sqlite3_open("test.db", &db);
if(rc){
fprintf(stderr, "Can't open database: %s\n", sqlite3_errmsg(db));
sqlite3_close(db);
exit(1);
}
if(rc!=SQLITE_OK){
fprintf(stderr, "SQL error: %s\n", zErrMsg);
}
printf("closing test.db\n");
sqlite3_close(db);
return 0;
}
To build this with the external libraries I have the makefile below. This will have to be adjusted for your toolchain path. In this example I placed the headers in external/include and the library in external/lib.
CC=/opt/arm-2008q3/bin/arm-none-linux-gnueabi-gcc
CFLAGS=-c -Wall
all: sqlitetest
sqlitetest: sqlitetest.o
$(CC) sqlitetest.o external/lib/libsqlite3.so.0 -o sqlitetest
sqlitetest.o: sqlitetest.c
$(CC) $(CFLAGS) sqlitetest.c -Iexternal/include/
clean:
rm -rf *o sqlitetest.o sqlitetest
You can then copy this directly to the board and execute it. There are many ways to transfer the compiled binaries to the board. Using a network filesystem such as sshfs or NFS will be the simplest to use if you are frequently updating data, but will require more setup. See your linux distribution's manual for more details. The simplest network method is using ssh/sftp. You can use winscp if from windows, or scp from linux. Make sure you set a password from debian for root or set up a shared key. Otherwise the ssh server will deny connections. From winscp, enter the ip address of the SBC, the root username, and the password you have set or the use of a shared key. This will provide you with an explorer window you can drag files into.
| Note: | Setting up a password for root is only feasible on the uSD image. |
For scp in linux, run:
#replace with your app name and your SBC IP address
scp sqlitetest root@192.168.0.50:/root/
After transferring the file to the board, execute it:
ts:~# ./sqlitetest
opening test.db
closing test.db
Compile the Kernel
For adding new support to the kernel, or recompiling with more specific options you will need to have an X86 compatible linux host available that can handle the cross compiling. Compiling the kernel on the board is not supported or recommended. Before building the kernel you will need to install a few support libraries on your workstation:
Prerequisites
RHEL/Fedora/CentOS:
yum install ncurses-devel ncurses
yum groupinstall "Development Tools" "Development Libraries"
Ubuntu/Debian:
sudo apt-get install build-essential libncurses5-dev libncursesw5-dev git
## If you are on a 64-bit system then 32-bit libraries will be required for the toolchain
# sudo apt-get install ia32-libs
# On newer distributions with Multiarch support:
#sudo dpkg --add-architecture i386
#sudo apt-get update
#sudo apt-get install libc6-dev:i386 zlib1g-dev:i386
For other distributions, please refer to their documentation to find equivalent tools.
Set up the Sources and Toolchain
# Download the cross compile toolchain (EABI)from Technologic Systems:
wget ftp://ftp.embeddedTS.com/ts-socket-macrocontrollers/ts-4700-linux/cross-toolchains/arm-2008q3.tar.gz
# Extract the toolchain
tar xvf arm-2008q3.tar.gz
# Move arm-2008q3 to a permanent location, eg /opt/toolchains/
mkdir /opt/toolchains/
mv arm-2008q3 /opt/toolchains/
# Download the Kernel sources
git clone https://github.com/embeddedTS/linux-2.6.34-ts471x.git
cd linux-2.6.34-ts471x
# Set the CROSS_COMPILE variable to the absolute path to the toolchain.
export CROSS_COMPILE=/opt/toolchains/arm-2008q3/bin/arm-none-linux-gnueabi-
export ARCH=arm
# This sets up the default configuration that we ship with for the TS-471x
make ts471x_defconfig
Once you have the configuration ready you can make your changes to the kernel. Commonly a reason for recompiling is to add support that was not built into the standard image's kernel. You can get a menu to browse available options by running:
make menuconfig
You can use the "/" key to search for specific terms through the kernel.
Build the kernel
Once you have it configured you can begin building the kernel. This usually takes about 5-10 minutes.
make
The new kernel will be at "arch/arm/boot/Image".
Install the Kernel and Modules
Install the target SD card in your workstation, and mount the Debian partition. For example, if your workstation's SD card is /dev/sdb:
# Update this to point to your SD card block device
export DEV=/dev/sdb
sudo mkdir /mnt/sd/
sudo dd if=arch/arm/boot/zImage of="$DEV"1 conv=fsync
sudo mount "$DEV"2 /mnt/sd/
INSTALL_MOD_PATH=/mnt/sd/ sudo -E make modules_install
INSTALL_HDR_PATH=/mnt/sd/ sudo -E make headers_install
sudo umount /mnt/sd/
sync
Build compat-drivers (optional)
Optionally if you use the WIFI-N-USB2 module or another recent USB wireless device you can build "compat-drivers" which provides more recent compatibility on this kernel.
# Assuming you are still in the 2.6.34 kernel directory
cd ../
export ARCH=arm
export CROSS_COMPILE=/opt/toolchains/arm-2008q3/bin/arm-none-linux-gnueabi-
# Update this to point to your SD card block device
export DEV=/dev/sdb
export KLIB=/mnt/sd
# Update these paths to point to the linux tree
export KLIB_BUILD=../linux-2.6.34-ts471x/
wget http://www.kernel.org/pub/linux/kernel/projects/backports/stable/v3.8.3/compat-drivers-3.8.3-2-snpu.tar.bz2 && \
tar xf compat-drivers-3.8.3-2-snpu.tar.bz2 && \
cd compat-drivers-3.8.3-2-snpu/ && \
make && \
sudo mount "$DEV"2 /mnt/sd/ && \
INSTALL_MOD_PATH=/mnt/sd/ sudo -E make install-modules && \
sudo umount /mnt/sd/ && \
sync
Using the Oracle JRE
Oracle provides a headless JRE binary for the ARMv5 processor series which is compatible with this processor. In many cases the OpenJDK JRE is sufficient for an application, but Oracle's JRE provides better performance. To install this JRE, first accept the license and download this from Oracle here.
Your version number may be slightly different, but the process should remain the same:
tar -xf ejre-7u45-fcs-b15-linux-arm-sflt-headless-26_sep_2013.tar.gz
mv ejre1.7.0_45/ /usr/share/oracle-jre/
ln -s /usr/share/oracle-jre/bin/java /usr/bin/java
You can verify this is installed by checking the version:
root@ts:~# java -version java version "1.7.0_45" Java(TM) SE Embedded Runtime Environment (build 1.7.0_45-b15, headless) Java HotSpot(TM) Embedded Client VM (build 24.45-b08, mixed mode)
Features
CPU
The TS-4710 supports the PXA166 from Marvell's Armada 100 series. The common features will be described in other sections, but for more details see the CPU user guide.
| Feature | PXA166 (88AP166) |
|---|---|
| Frequency | 800MHz |
| Video Playback Acceleration (gstreamer) | Supported up to D1 |
| Maximum Framebuffer Resolution | Up to WUXGA |
MicroSD Card Interface
This System-on-Module (SoM) uses our SD controller implementation which supports microSD, microSDHC, and microSDXC cards. This controller has been tested with Sandisk Extreme SD cards which allow read speeds up to 20.5MB/s, and write speeds up to 21.5MB/s.
The support for the SD controller is provided by sdctl which serves up a /dev/nbd0 for the entire block device. The kernel also includes a module that will break this up into partitions. Our default software image contains 2 partitions:
| Device | Contents |
|---|---|
| /dev/nbd0 | SD Card block device |
| /dev/nbd0p1 | Kernel and initramfs |
| /dev/nbd0p2 | Full Linux Root |
DoubleStore
This series supports DoubleStore which can be used to significantly increase the reliability of SD cards. This allows one SD image to be written to two cards allowing redundancy among both SD cards. See our white paper for more information on the concept. Development can take place with a single MicroSD card, but for using DoubleStore 2 MicroSD cards are used.
The default SD image is 3GB which is designed to fit in a dual-card Doublestore configuration. When dual card doublestore is used it stores the same image on both cards and also includes metadata and checksums for the entire image.
You can use the dblstorctl utility to work with DoubleStore on your Linux workstation. The simplest way to get doublestore set up is to first take a backup of your SD image, and then use dblstorctl on a workstation to convert it:
export INPUTIMAGE="yourimagebackup.dd"
eval $(stat -c "imgsize=%s" $INPUTIMAGE)
dblstorctl --primary ${INPUTIMAGE}.dblstor --fallback ${INPUTIMAGE}.dblstor.fallback --init --writeimg "$INPUTIMAGE" --size=${imgsize}B
This will output yourimagebackup.dd.dblstor which can be written directly to both SD cards:
dd if=yourimagebackup.dd.dblstor bs=4M conv=fsync of=/dev/sdb # replace sdb with your SD card device
The board will boot the same using the DoubleStore MicroSD cards, but sdctl includes additional information:
# sdctl --stats nbdpid=338 nbd_readreqs=1508 nbd_read_blks=95490 nbd_writereqs=0 nbd_write_blks=0 nbd_seek_past_eof_errs=0 sdcard_resets=4 read_seeks=1261 write_seeks=0 size=0x641800 humanized_size=3.35GB fb_offset=-6559744 primary_tainted=0 primary_failed=0 fallback_tainted=0 fallback_failed=0 resilver_pct_done=0 lifetime_write_blks=59038888 humanized_lifetime_write_blks=30.22GB errors=0 unrecoverable_errors=0 conflicts=0 fallback_configuration="separate disk"
fallback_configuration should read "seperate disk" when booting doublestore correctly. For diagnostics, the tainted and failed settings are the most relevant:
primary_tainted=0 primary_failed=0 fallback_tainted=0 fallback_failed=0
When a card is tainted, the LED near the card will begin to blink. This indicates Doublestore has seen the card perform an unexpected behavior that DoubleStore was able to correct.
Interrupts
We include a userspace IRQ patch in our kernels. This allows you to receive interrupts from your applications where you would normally have to write a kernel driver. This works by creating a file for each interrupt in '/proc/irq/<irqnum>/irq'. The new irq file allows you to block on a read on the file until an interrupt fires.
The original patch is documented here.
The Linux kernel supports up to 16 IRQs from the FPGA. When the CPU receives an IRQ from the FPGA, it uses the IRQ register in the #Syscon to find out which IRQ on the MUX is triggering. Currently only three IRQs are used. Off-board IRQs 5, 6, and 7 correspond to FPGA IRQs 0, 1, and 2, respectively. FPGA IRQs 3 to 15 are reserved for future uses. If the DIO pins are not being used as IRQs, they can be masked out by writing 0 to the corresponding bit in the IRQ mask register.
| IRQ # | Name | Socket Location |
|---|---|---|
| 49 | Combined GPIO Interrupt | Any MFP pin |
| 64 | XUART IRQ | N/A |
| 65 | CAN1 IRQ | N/A |
| 66 | CAN 2 IRQ | N/A |
| 67 | IRQ5/DIO_00[1] | CN1-93 |
| 68 | IRQ6/DIO_01[1] | CN1-91 |
| 69 | IRQ7/DIO_02[1] | CN1-89 |
| 70 | EVGPIO | N/A |
This example below will work with any of our products that support userspace IRQs. It opens the IRQ number specified in the first argument, and prints when it detects an IRQ.
#include <stdio.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
#include <sys/select.h>
#include <sys/stat.h>
#include <unistd.h>
int main(int argc, char **argv)
{
char proc_irq[32];
int ret, irqfd = 0;
int buf; // Holds irq junk data
fd_set fds;
if(argc < 2) {
printf("Usage: %s <irq number>\n", argv[0]);
return 1;
}
snprintf(proc_irq, sizeof(proc_irq), "/proc/irq/%d/irq", atoi(argv[1]));
irqfd = open(proc_irq, O_RDONLY| O_NONBLOCK, S_IREAD);
if(irqfd == -1) {
printf("Could not open IRQ %s\n", argv[1]);
return 1;
}
while(1) {
FD_SET(irqfd, &fds); //add the fd to the set
// See if the IRQ has any data available to read
ret = select(irqfd + 1, &fds, NULL, NULL, NULL);
if(FD_ISSET(irqfd, &fds))
{
FD_CLR(irqfd, &fds); //Remove the filedes from set
printf("IRQ detected\n");
// Clear the junk data in the IRQ file
read(irqfd, &buf, sizeof(buf));
}
//Sleep, or do any other processing here
usleep(10000);
}
return 0;
}
Any of the MFP pins can be repurposed to trigger IRQ 49. For example, to make MFP_46 (CN2_72) trigger on a rising edge:
# Enable rising edge detection on MFP_46
peekpoke 32 0xD4019034 0x4000
# Unmask MFP_46
peekpoke 32 0xD40190A0 0x4000
# to clear the interrupt after it has been triggered
peekpoke 32 0xD401904c 0x4000
See page 169 of the CPU manual for more information on the interrupt controller.
RTC
The RTC is accessed using tshwctl. This is automatically retrieved on startup, but must be set manually.
# Save the running system clock to the RTC
tshwctl --setrtc
# Set the system clock from the RTC
tshwctl --getrtc
NVRAM
The RTC has an included 128-byte battery-backed NVRAM which can be accessed using tshwctl. Its contents will remain with the main power off, so long as the RTC battery is installed and withing a valid voltage range.
tshwctl --nvram
This will return a format such as:
nvram0=0xf7f8a73e nvram1=0x2fef5ae0 nvram2=0x48ca4278 ... nvram31=0x70544510
This breaks up the NVRAM into 32 32-bit registers which can be accessed in bash. As this uses the name=value output, "eval" can be used for simple parsing:
eval `tshwctl --nvram`
echo $nvram2
From the above value, this would return 0x48ca4278. To set values, the respective environment variable name can be set:
nvram0=0x42 tshwctl --nvram
Note that the command 'tshwctl --nvram' will output the current contents of NVRAM before setting any new values. At this point, running 'tshwctl --nvram' once more will print the updated contents for verification. This can be used for reading a 32-bit quantity and updating it with a single command.
Temperature Sensor
This System-on-Module includes temperature sensors located on the CPU and RTC. Both of these can be read using tshwctl:
tshwctl --rtctemp
tshwctl --cputemp
Both of these will return the temperature in millicelsius.
LEDs
On all of our baseboards we include 2 indicator LEDs which are under software control. You can manipulate these using tshwctl --greenledon --redledon or tshwctl --greenledoff --redledoff. The LEDs have 4 behaviors from default software. The LEDs are also controllable via the Syscon register at offset 0x12.
| Green Behavior | Red behavior | Meaning |
|---|---|---|
| Solid On | Off | System is booted and running |
| Solid On | On for approximately 15s, then off | Once the system has booted the kernel and executed the startup script, it will check for a USB device and then determine if it is a mass storage device. This is used for updates/blasting through USB. Once it determines this is not a mass storage device the red LED will turn back off. |
| On for 10s, off for 100ms, and repeating | Turns on after Green turns off for 300ms, and then turns off for 10s | The watchdog is continuously resetting the board. This happens when the system cannot find a valid boot device, or the watchdog is otherwise not being fed. This is normally fed by tshwctl once a valid boot media has started. See the #Watchdog section for more details. |
| Off | Off | The FPGA is not able to start. Typically either the board is not being supplied with enough voltage, or the FPGA has been otherwise damaged. If a stable 5 V is being provided and the supply is capable of providing at least 1 A to the System-on-Module (SoM), an RMA is suggested. |
| Blinking about 5ms on, about 10ms off. | Blinking about 5ms on, about 10ms off. | The board is receiving too little power, or something is drawing too much current from the SoM's power rails. |
Web Interface
This System-on-Module includes a web interface that can be used to simplify common tasks when working with our embedded systems. Note that this is only available in the initramfs, and not the full Debian boot.
Uploading files
On the main page you can select a file and upload. These have various functions depending on the file extensions:
| Filename/Extension | Description |
|---|---|
| *.vme.bz2 | Upload FPGA to be soft reloaded automatically on startup. This will be copied to /ts/ path in the Linux root filesystem.
|
| ko.tar.bz2 | While most kernel modules will be loaded automatically when needed, if you include a ko.tar.bz2 this will insmod each file in the archive automatically on startup. This will be copied to the /ts/ path in the linux root filesystem.
|
| init | If this file exists and the JP1 is not set, the board will boot to the initramfs and execute this script. This can be used to have an application automatically run on startup without proceeding with the Linux root filesystem's traditionally lengthy startup. This can have an application running within seconds after power-on. The $PATH variable is set up to be able to resolve most applications in the Linux root filesystem, and the libraries of the full distribution are available. As this does not run through the normal startup, any running services or network configuration will need to be started manually. |
| Image, zImage, kernel*.dd | This will automatically replace the first partition containing the Kernel. |
| root*.dd | This will completely replace the second partition with the uploaded dd file. |
| mbr.dd|mbr*.dd | Replace the MBR on the current boot image. |
| *.dd | Any file not caught by one of the previous *.dd filenames will entirely replace the SD image.
|
| *.sh | Any file named *.sh will automatically be copied to /tmp, set as executable and run.
|
| root*.tar | This will remove all data from the Linux root filesystem and replace it with the contents of the uploaded root*.tar file.
|
| src*.tar | This will extract the contents to the /ts/ directory in the Linux root filesystem and if present, execute the Makefile. This could be used to build a project, and automatically install it.
|
| *.c *.cpp | Any uploaded C/C++ file will automatically be compiled and executed. The applications stdout will be printed out to the web page.
|
| * | Any other files not captured by a previous pattern will be copied to the /ts/ path in the Linux root filesystem.
|
Any uploaded file can be compressed with bzip2 or gzip before uploading. The file will be decompressed and then processed as normal as described in the above table.
Downloading Files
On the main page there is a download link for 4 files. Any downloaded file will be renamed to contain the date in the format date -Iminutes.
| Filename | Description |
|---|---|
| backup.dd | This is a backup containing the MBR, Kernel/initramfs, and Linux root filesystem. |
| root.dd | This is a backup of a complete dd of the Linux root filesystem. |
| root.tar | The root.tar contains a complete tar of the contents in the root filesystem. |
| kernel.dd | This file contains a copy of the kernel and initramfs. |
Duplicating an SD card
This page can be used to either duplicate an SD card, or convert a software image to a single or dual DoubleStore card configuration. When this page is loaded it copies the kernel/initramfs to ram. You will need to have the root.tar downloaded before continuing.
Once you have loaded this page and you have a copy of the root.tar, you can either remove the current SD card, or leave it in if you intend to convert it to DoubleStore. On step 2, you can select "Standard" to write a new SD card without DoubleStore, or you can create a single or dual card configuration. Click "Format card" after selecting either option.
After being formatted you can upload the root*.tar file to reformat the rest of the card. Once this is completed, you can reboot to test out the card, or restart the procedure to create another card.
Find other TS-41XX devices
By default this board broadcasts itself using multicast DNS which can be used to detect all other similar boards on the network. This will print out the last 6 of the MAC address which can be used to uniquely identify each board.
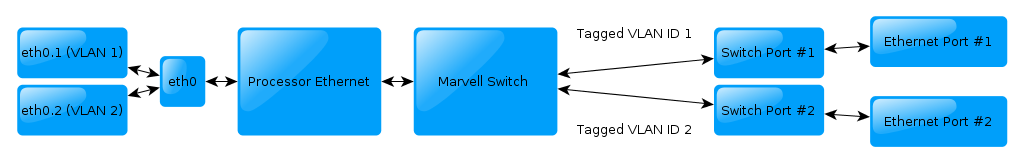
Ethernet Port
The Marvell Processor implements a 10/100 ethernet controller with support built into the Linux kernel. The TS-4712 and TS-4720 include an integrated Marvell Ethernet switch that allows multiple interfaces from one 10/100 port. This allows a total bandwidth of 100MB/s between both ports.
|
The default configuration will have the ports act as 2 individual ports on baseboards where this is supported. When in this mode all network traffic should be directed to eth0.1 and eth0.2, but not eth0 which will not be forwarded outside of the switch. When using the network with the VLAN mode you should not attempt to configure eth0, but instead only use eth0.1 or eth0.2. On baseboards where the second port supports the VLAN ethernet, you can modify /ts/config
CFG_2ETH="2"
On the next boot the eth0.1 and eth0.2 ports will not be present. In this case the switch is configured to transparently pass through packets rather than configuring the VLANs, so eth0 should be used.
| Note: | Some baseboards create 2 Ethernet ports using a USB Ethernet controller which will not be integrated with this switch. This includes the TS-8100, TS-8390, and TS-8900. In this case the Ethernet switch is configured to pass through packets which will only use eth0. |
You can use standard Linux utilities such as ifconfig/ip to control eth0 and the vlan interfaces. See the #Configuring the Network section for more details. For the specifics of this interface see the CPU manual.
The switch ports can also use tshwctl to detect link and the negotiated link speed:
root@ts4712-f7c0ff:~# tshwctl --ethinfo baseboard_model=0xa baseboard=8900 baseboard_rev=A switch_model=88E6020 switch_ports=a b switchporta_link=0 switchporta_speed=10HD switchportb_link=1 switchportb_speed=100FD
By default the VLAN configuration mode is only enabled when a recognized baseboard is connected. To use this on a custom baseboard you would need to modify /ts/config and use the option:
CFG_2ETH="1"
NOTE:
Even using VLAN configuration, both ports have the same MAC address. In most intended conditions this is OK because the network on either port is never expected to encounter the network on the other. However, there are some very rare network conditions where this situation is possible. For this condition, Technologic Systems has reserved a second MAC address for each TS-SOCKET device, this address is always the current MAC incremented by 1. Consult your network system administrator or email support@embeddedTS.com if you require assistance with this setting.
DIO
This board uses both CPU and a DIO controller in the FPGA.
The CPU DIO typically has 1-7 functions associated with various pins (I2C, PWM, SPI, etc). See the CPU manual for the complete listing and for information on how to control these DIO. For purposes of identity, all FPGA DIO will be labelled DIO_n (where n is the DIO pin number), and all CPU dio will be labelled MFP_n.
CPU DIO
Full details on CPU pins can be found in the CPU manual, along with mode and mapping assignments specific to the CPU. The MFP pins can have multiple functions and not all default to GPIO, so understanding each one you wish to modify is important to your development process. The MFP definition registers are described in the CPU manual starting in Section A1, pages A7 through A12 (note these are appendix pages). This wiki will assume the reader already has a thorough understanding of these settings and is comfortable moving forward using them as a GPIO. NOTE: The default TS boot scripts set some MFP pins up with functions other than the default functionality. It is important to set the MFP you wish to use to the function you desire before using it. Do not assume default functionality is present on all MFP pins. The base address for the MFP alternate function block is at 0xD401E000, each MFP pin has its own address as listed in the table starting on page A-7. Alternate function definitions start in the table on page 58.
The CPU GPIO are divided into four banks, GPIO bank 0 through 3. These banks are controlled by several registers. Full information on these registers is found in the CPU manual starting at page A-832. The most important registers for general GPIO usage are the bit-value register (GPIO_GPLR / GPIO_PLR0-3), the GPIO direction register (GPIO_GPDR / GPIO_PDR0-3), the GPIO Output Set register (GPIO_GPSR / GPIO_GPIO_PSR0-3), and the GPIO Output Clear Register (GPIO_GPCR / GPIO_PCR0-3). The GPIO section in the CPU manual contains a typo in the GPIO control base address. The correct base address is 0xD4019000.
It can be generally assumed MFP # and GPIO bit # are identical for the purposes of this table.
| Register Name | Address Offset | GPIO Start (bit 0) | GPIO End (bit 31) | Function |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| GPIO_PLR0 | 0x0000 | 0 | 31 | DIO Data (RO) |
| GPIO_PLR1 | 0x0004 | 32 | 63 | |
| GPIO_PLR2 | 0x0008 | 64 | 95 | |
| GPIO_PLR3 | 0x0100 | 96 | 122 | |
| GPIO_PDR0 | 0x000c | 0 | 31 | DIO Direction |
| GPIO_PDR1 | 0x0010 | 32 | 63 | |
| GPIO_PDR2 | 0x0014 | 64 | 95 | |
| GPIO_PDR3 | 0x010c | 96 | 122 | |
| GPIO_PSR0 | 0x0018 | 0 | 31 | DIO Set |
| GPIO_PSR1 | 0x001c | 32 | 63 | |
| GPIO_PSR2 | 0x0020 | 64 | 95 | |
| GPIO_PSR3 | 0x0118 | 96 | 122 | |
| GPIO_PCR0 | 0x0024 | 0 | 31 | DIO Clear |
| GPIO_PCR1 | 0x0028 | 32 | 63 | |
| GPIO_PCR2 | 0x002c | 64 | 95 | |
| GPIO_PCR3 | 0x0124 | 96 | 122 |
There are also edge-detect registers that work via set and status bits documented in the CPU manual, see section A.36.5 starting at page A-386.
FPGA DIO
All FPGA DIO are controlled by three distinct register types: Direction, Input Data, and Output Data. To use any DIO pin, the direction register must be set (0 for input, 1 for output), then either the input register may be read, or the output register may be written to. These registers are described in the Syscon memory table.
For example, to write to DIO_0, bit 0 (the LSB) of 0x80004018 (The direction register for DIO_0 through DIO_14) must be set high, then the desired value (high = 1 low = 0) should be written to bit 0 of 0x80004010 (the Output Data register for DIO_0 through DIO_14). Alternatively to read the status of that pin, the Direction Register must be set low, then bit zero of 0x80004020 would reflect the status of that pin.
All 60 of the DIO from the FPGA will default to the DIO mode. These pins coming from the FPGA are all 3.3V tolerant. To manipulate these DIO you can access the #Syscon.
Bit masking: Any bits not expressly mentioned here should be masked out. Direction setting: 0 is input, 1 is output.
For simple operations you can use tshwctl to set the FPGA DIO pins:
# Set DIO 30 as a high output
tshwctl --setdio 30
# Set DIO 30 as a low output
tshwctl --clrdio 30
# Read the input value of DIO 42, 43, 44
# This will set the pin to an input and return the value
tshwctl --getdio 42,43,44
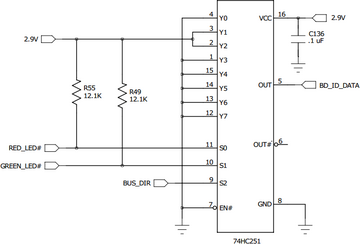
Baseboard ID
All of our off the shelf baseboards contain a hard wired 3-state 8-input multiplexers. This is not required to implement in custom baseboards, but it can be useful to identify the board in software. During startup of the System-on-Module, 4 DIO are used to obtain the baseboard model ID. The red LED (CN2_06) is state 0, green LED (CN2_08) is state 1, BUS_DIR (CN1_98) is state 2, and BD_ID_DATA (CN1_83) is used for data.
The first 6 lines are used as the six bits that define the baseboard. The last two lines (Y6 & Y7 in the schematic image below) define the bits to indicate the board revision.
You can find example code for accessing the baseboard ID in tshwctl. For example, "tshwctl -B" will return "baseboard_model=" with the detected baseboard.
For custom baseboards we have reserved the address 42 which will never be used by our standard products.
| ID | Baseboard |
|---|---|
| 0 | TS-8200 |
| 1 | Reserved, do not use |
| 2 | TS-TPC-8390 |
| 4 | TS-8500 |
| 5 | TS-8400 |
| 6 | TS-8160 |
| 7 | TS-8100 |
| 8 | TS-8820-BOX |
| 9 | TS-8150 |
| 10 | TS-TPC-8900 |
| 11 | TS-8290 |
| 13 | TS-8700 |
| 14 | TS-8280 |
| 15 | TS-8380 |
| 16 | TS-AN20 |
| 17 | TS-TPC-8920 |
| 19 | TS-8550 |
| 20 | TS-TPC-8950 |
| 22 | TS-8551 |
| 42 | Reserved for customer use, never used by us |
| 63 | TS-8200 |
USB
USB OTG
This board features USB OTG which allows you to use the USB port as either a host, or a device. Much of the USB OTG framework is described here. You will need to recompile your kernel to include these modules.
The OTG driver from Marvell has a caveat attached to it, whenever the OTG port is to be used as a host the following command needs to be issued after the device is plugged in:
echo 1 > /proc/driver/otg
Device mode of OTG will function without having to write to the above proc file.
| Note: | When paired with the TS-8160 the OTG port is exposed as the lower USB host A port. Because of this the above command needs to be run whenever a USB device is attached to the port in order to tell the OTG driver to enter host mode and communicate with the USB device. |
USB Host
The USB host port is a standard USB 2.0 at 480Mbps. The Linux kernel provides most of the USB support, and some devices may require a kernel recompile. Common devices such as keyboards, mice, wifi, and ethernet should mostly work out of the box.
The libusb project can also be used to communicate directly with USB peripherals from userspace.
TWI
These pins provide a standard two-wire interface. This bus also connects to an RTC on the System-on-Module. MFP105 and MFP106 can be used as a second TWI bus directly from the CPU. For more information, see the CPU manual here.
SPI
The SPI controller is implemented in the FPGA. This core is found at 0x80004800, and should only be accessed using 16-bit reads/writes.
The table below is the register map for the SPI in the FPGA:
| Offset | Access | Bit(s) | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0x0 | Read Only | 15 | SPI MISO state |
| Read/Write | 14 | SPI CLK state | |
| Read/Write | 13:10 | Speed - 0 (highest), 1 (1/2 speed), 2 (1/4 speed)... | |
| Read/Write | 9:8 | LUN (0-3 representing the 4 chip selects) | |
| Read/Write | 7 | CS (1 - CS# is asserted) | |
| N/A | 6:1 | Reserved | |
| Read/Write | 0 | Speed | |
| 0x2 | Read Only | 15:0 | Previous SPI read data from last write |
| 0x4 | N/A | 15:0 | Reserved |
| 0x6 | N/A | 15:0 | Reserved |
| 0x8 | Read/Write | 15:0 | SPI read/write with CS# to stay asserted |
| 0xa | Read Only | 15:0 | SPI pipelined read with CS# to stay asserted |
| 0xc | Read/Write | 15:0 | SPI Read/Write with CS# to deassert post-op |
| 0xe | N/A | 15:0 | Reserved |
The SPI clk state register should be set when CS# is deasserted. Value 0 makes SPI rising edge (CPOL=0), 1 is falling edge (CPOL=1). This only applies to speed >= 1.
Where the base clock is 75Mhz (extended temp alters this to 50Mhz), speed settings break down as follows:
| Value | Speed |
|---|---|
| 0 | 75Mhz |
| 1 | 37.5MHz |
| 2 | 18.75MHz |
| 3 | 12.5MHz |
| 4 | 9.375MHz |
| 5 | 7.5MHz |
| 6 | 6.25MHz |
| 7 | 5.36MHz |
| 8 | 4.68MHz |
| 9 | 4.17MHz |
| 15 | 2.5MHz |
| 19 | 1.97MHz |
| 31 | 1.21MHz |
The pipelined read register is for read bursts and will automatically start a subsequent SPI read upon completion of the requested SPI read. Reading from this register infers that another read will shortly follow and allows this SPI controller "a head start" on the next read for optimum read performance. This register should be accessed as long as there will be at least one more SPI read with CS# asserted to take place.
FPGA
All macrocontrollers feature an FPGA. Any external interfaces called for by the TS-SOCKET specification that are not provided by the CPU are implemented in the FPGA whenever possible. The FPGA is connected to the CPU by a static memory controller, and as a result the FPGA can provide registers in the CPU memory space.
While most common functionality is accessed through layers of software that are already written, some features may require talking directly to the FPGA. Access to the FPGA is done through either the 8-bit or 16-bit memory regions. Code should access 16-bit or 8-bit depending on the access designed for the specific hardware core. For example, the CAN core is 8 bit, the 8 bit MUXBUS space is 8 bit, and some 8 bit cycles are needed for the SPI core if you want to do 8 bit SPI transactions. To access hardware cores in the FPGA, add the offset in the table below to the base address.
| Bit Width | Base Address |
|---|---|
| 16 | 0x80000000 |
| 8 | 0x81000000 |
| Offset | Usage | Bit Width |
|---|---|---|
| 0x0000 | 16KB blockram access (for XUART buffer) | 16 |
| 0x4000 | Syscon registers | 16 |
| 0x4400 | ADC registers (for off-board ADC) | 16 |
| 0x4800 | SPI interface | 16 |
| 0x4C00 | CAN controller | 8 |
| 0x4D00 | 2nd CAN controller | 8 |
| 0x5000 | Touchscreen registers | 16 |
| 0x5400 | XUART IO registers | 16 |
| 0x8000 | 32KB MUXBUS space | 16/8 |
FPGA Bitstreams
The FPGA has the capability to be reloaded on startup and reprogram itself with different configurations. The default bitstream is hardcoded into the FPGA, but the soft reloaded bitstreams can be placed in /ts/ts<model>-fpga.vme.gz on the Debian root to make the board load the bitstream on startup. If we do not have a configuration you need, you can build a new bitstream, or contact us for our engineering services.
| Bitstream | XUARTs | CAN | Touchscreen | SPI | ADC |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Default (8K LUT) | 0-6 | On | On | On | Off |
| ts4710-fpga-rev4-default-ADC.vme.bz2 | 0-6 | On | On | On | On |
FPGA Programming
| Note: | We do not provide support for the opencores under our free support, however we do offer custom FPGA programming services. If interested please contact us. |
We provide an open version of the Verilog project that contains the functionality of the default FPGA bitstream. The FPGA bitstream is built using Lattice Diamond which is free and runs under Windows or Linux (Redhat). This allows you to modify the verilog and create a jedec file with your custom logic. The jedec is converted to a vme file which is loaded from the SD card and used to reprogram the SRAM of the FPGA on every startup. This requires approximately a second during startup to reprogram, but allows you to recover by removing the bitstream file from the SD card in the case of a faulty bitstream.
The opencore FPGA sources are available here. These sources are supported on the TS-4710, TS-4712, and TS-4720. Custom logic can be built by implementing a wishbone compatible core, or by extending the cores we already have connected.
The ts4710_top.v file is used to connect all of the wishbone cores, and map any DIO. The syscon.v is used for most common system configuration registers. As a simple example these next steps will modify the custom load register located at 0x2a in the syscon.v.
Open up the Lattice diamond tools and open the .ldf file to open the project. On the bottom left there are 3 tabs to control the left panel (Files, Process, and Hierarchy). Go to Files, and double click syscon.v. Around line 40 is:
localparam [3:0] revision = 4'h2;
localparam [15:0] custom = 16'h0000;
You can edit the custom value to:
localparam [15:0] custom = 16'h0001;
The custom register is not used by any default software and is a safe register to use for a custom version number. The default bitstream will always use 0.
Save the file and go to the "Process" tab. Double click "Place & Route Trace" to begin synthesizing the bitstream. This will take approximately 5-10 minutes. Once this is finished open the "Reports" tab from the top open file list. Under "Analysis Reports" click on "Place & Route Trace". This is used to verify timing of your build. Under "Preference Summary" make sure none of the clock domains list errors. If timing is not met this will cause seemingly random issues with the bitstream which will usually present first as SD corruption.
Once the timing has been verified, double click "JECEC File" on the "Process" tab to build the jed file. Once this is finished there will be a "ts4710_default.jed" in the project folder. In order for the board to use this it must be converted to a vme file. This is generated using "jed2vme":
jed2vme ts4710_default.jed | bzip2 > ts4710-fpga.vme.bz2
| WARNING: | Generating a VME using other Lattice's tools can generate a flash bitstream which will render your board unbootable. |
Once this is built it should be placed on the second partition of the SD card as "/ts/ts<model>-fpga.vme.bz2" This should match the device's model such as "/ts/ts4710-fpga.vme.bz2".
Once it is loaded on the SD card the board can be booted normally. The green and red LEDs will shut off during programming, and then turn back on after the bitstream has been reloaded. Commands should not be run during reload since issuing a bus cycle during programming can interfere with timing and cause the reload to fail. Once it has reloaded you can use devmem to verify the register has changed:
devmem 0x8000802a 16
On the default bitstream this should return "0x0000", or "0x0001" if modified as suggested above.
Syscon
The registers listed below are all 16 bit registers and must be accessed with 16 bit reads and writes. This register block appears at base address 0x80004000. For example, to identify the model:
devmem 0x80004000 16
This will return 0x4710, 0x4712, 0x4720, or 0x4740 depending on the model.
Many of the syscon options can be manipulated using tshwctl.
Usage: tshwctl [OPTION] ... Technologic Systems TS-471x / TS-77XX FPGA manipulation. General options: -g, --getmac Display ethernet MAC address -s, --setmac=MAC Set ethernet MAC address -R, --reboot Reboot the board -t, --getrtc Get system time from RTC time/date -S, --setrtc Set RTC time/date from system time -F, --rtcinfo Print RTC temperature, poweron/off time, etc -v, --nvram Get/Set RTC NVRAM -i, --info Display board FPGA info -e, --greenledon Turn green LED on -b, --greenledoff Turn green LED off -c, --redledon Turn red LED on -d, --redledoff Turn red LED off -D, --setdio=<pin> Sets DDR and asserts a specified pin -O, --clrdio=<pin> Sets DDR and deasserts a specified pin -G, --getdio=<pin> Sets DDR and gets DIO pin input value -x, --random Get 16-bit hardware random number -W, --watchdog Daemonize and set up /dev/watchdog -n, --setrng Seed the kernel random number generator -X, --resetswitchon Enable reset switch -Y, --resetswitchoff Disable reset switch -l, --loadfpga=FILE Load FPGA bitstream from FILE -q, --cputemp Display the CPU die temperature -U, --removejp=JP Remove soft jumper numbered JP (1-8) -J, --setjp=JP Set soft jumper numbered JP (1-8) -k, --txenon=XUART(s) Enables the TX Enable for an XUART -K, --txenoff=XUART(s) Disables a specified TX Enable -N, --canon=PORT(s) Enables a CAN port -f, --canoff=PORT(s) Disables a CAN port -h, --help This help -j, --bbclkon Enables a 12.5MHz clock on DIO 3 -H, --bbclkoff Disables the 12.5MHz clock -E, --bbclk2on Enables a 25MHz clock on DIO 34 -I, --bbclk2off Disables the 25MHz clock -r, --touchon Turns the touchscreen controller on -T, --touchoff Turns the touchscreen controller off -B, --baseboard Display baseboard ID -a, --adc Display MCP3428 ADC readings in millivolts -P, --ethvlan Configures a network switch to split each port individually in a vlan -y, --ethswitch Configures a network switch to switch all of the outside ports to one interface -e, --ethwlan Configures the first network port (A) to its own VLAN, and all other ports to a shared switch -C, --ethinfo Retrieves info on the onboard switch
| Offset | Bits | Usage |
|---|---|---|
| 0x00 | 15:0 | Returns board model, eg 0x4710 = TS-4710 |
| 0x02 | 15 | Reset switch enable (Use DIO 9 input) |
| 14 | Enable touchscreen (override DIO 30-35) | |
| 13 | Enable UART4 TXEN (override DIO 14) | |
| 12 | Enable UART0 TXEN (override DIO 12) | |
| 11 | Enable 12.5MHz base board clock (override DIO 3) | |
| 10 | Enable SPI (override DIO 17-20) | |
| 9 | Enable 2nd CAN (override DIO 10,11) | |
| 8 | Enable CAN (override DIO 15,16) | |
| 7:6 | Scratch Register | |
| 5 | Mode2 | |
| 4 | Mode1 | |
| 3:0 | FPGA revision | |
| 0x04 | 15:0 | Muxbus configuration register |
| 0x06 | 15:0 | Watchdog feed register |
| 0x08 | 15:0 | Free running 1MHz counter LSB |
| 0x0a | 15:0 | Free running 1MHz counter MSB |
| 0x0c | 15:0 | Hardware RNG LSB |
| 0x0e | 15:0 | Hardware RNG MSB |
| 0x10 | 15 | Baseboard 25MHz Clock (override DIO 34) |
| 14:0 | DIO 14:0 output data | |
| 0x12 | 15:14 | Reserved |
| 13 | Enable alternate touch controller pins | |
| 12 | Red LED (1 = on) | |
| 11 | Green LED (1 = on) | |
| 10:6 | DIO 26:22 output data | |
| 5:0 | DIO 20:15 output data | |
| 0x14 | 15:0 | DIO 42:27 output data |
| 0x16 | 15 | Enable UART2 TXEN (override DIO 10) |
| 14 | Enable UART1 TXEN (override DIO 8) | |
| 13 | Enable UART5 TXEN (override DIO 7) | |
| 12 | Enable UART3 TXEN (override DIO 13) | |
| 11:0 | DIO 59:48 output data | |
| 0x18 | 15 | Reserved |
| 14:0 | DIO 14:0 data direction | |
| 0x1a | 15:11 | Reserved |
| 10:6 | DIO 26:22 data direction | |
| 5:0 | DIO 20:15 data direction | |
| 0x1c | 15:0 | DIO 42:27 data direction |
| 0x1e | 15:12 | Reserved |
| 11:0 | DIO 59:48 data direction | |
| 0x20 | 15 | Reserved |
| 14:0 | DIO 14:0 input data | |
| 0x22 | 15:11 | Reserved |
| 10:6 | DIO 26:22 input data | |
| 5:0 | DIO 20:15 input data | |
| 0x24 | 15:0 | DIO 42:27 input data |
| 0x26 | 15:12 | Reserved |
| 11:0 | DIO 59:48 input data | |
| 0x28 | 15:4 | Reserved |
| 3:0 | FPGA TAG memory access [1] | |
| 0x2a | 15:0 | Custom load ID register [2] |
| 0x2c | 15:6 | Reserved |
| 5 | Offboard IRQ 7 | |
| 4 | Offboard IRQ 6 | |
| 3 | Offboard IRQ 5 | |
| 2 | CAN2 IRQ | |
| 1 | CAN IRQ | |
| 0 | XUART IRQ | |
| 0x2e | 15:6 | Reserved |
| 5 | Offboard IRQ 7 mask (1 disabled, 0 on) [3] | |
| 4 | Offboard IRQ 6 mask (1 disabled, 0 on) [3] | |
| 3 | Offboard IRQ 5 mask (1 disabled, 0 on)[3] | |
| 2 | CAN2 IRQ mask (1 disabled, 0 on)[3] | |
| 1 | CAN IRQ mask (1 disabled, 0 on)[3] | |
| 0 | XUART IRQ mask (1 disabled, 0 on)[3] | |
| 0x34 | 0 | Enable 14.3MHz baseboard clock on DIO 3 |
| 1 | USB 5V disable [4] | |
| 2 | LCD 3.3V disable [5] |
- ↑ TAG memory stores persistent data on the FPGA such a the MAC address, CPU settings, and the born on date. Software using this data should instead use tshwctl rather than accessing this register manually.
- ↑ Reads back 0 on default load. Used to identify customized bitstreams
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 3.2 3.3 3.4 3.5 The IRQ masks are handled automatically by the kernel after an IRQ is requested. Under most circumstances these registers should not be manipulated.
- ↑ This toggles a DIO on CN1_04 and requires offboard circuitry on the baseboard to toggle USB power.
- ↑ This toggles a DIO on CN1_48 and requires offboard circuitry on the baseboard to toggle LCD power.
ADC Core
The FPGA includes a core for communicating with the MCP3428 ADC controller we use on several of our baseboards. If you are using this on your own baseboard this core assumes the standard circuit which allows 2 differential channels and 4 single-ended channels. The single-ended channels are chosen using analog muxes controlled by the AN_SEL line. Since different baseboards use a different pin for AN_SEL, a register is also provided to select the correct lines. Channels 1 and 2 are differential channels with a range of -2.048V to +2.048V. Channels 3-6 are 0 to 10.24V.
This example prints out all 6 ADC readings in millivolts:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <sys/mman.h>
#include <sys/stat.h>
#include <assert.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
#define peek16(adr) PEEK16((unsigned long)&syscon[(adr)/2])
#define poke16(adr, val) POKE16((unsigned long)&syscon[(adr)/2],(val))
static volatile unsigned short *syscon;
static inline unsigned short PEEK16(unsigned long addr) {
unsigned short ret;
asm volatile (
"ldrh %0, [ %1 ]\n"
: "=r" (ret)
: "r" (addr)
: "memory"
);
return ret;
}
static inline void POKE16(unsigned long addr, unsigned short dat) {
asm volatile (
"strh %1, [ %0 ]\n"
:
: "r" (addr), "r" (dat)
: "memory"
);
}
int main()
{
int x, i, devmem;
// Map the Syscon core
devmem = open("/dev/mem", O_RDWR|O_SYNC);
assert(devmem != -1);
syscon = (unsigned short *) mmap(0, 4096, PROT_READ | PROT_WRITE, MAP_SHARED, devmem, 0x80004000);
//// Select AN_SEL line:
//// If you have a TS-TPC-8390 baseboard:
poke16(0x400, 0x28);
//// TS-8160/TS-8100
//poke16(0x400, 0x18);
//// if unknown baseboard, uses no an_sel
//// but assumes ADC is there
//poke16(0x400, 0x08);
// enable all 6 channels
poke16(0x402, 0x3f);
// allow time for conversions
usleep(500000);
for (i = 1; i <= 6; i++) {
x = (signed short)peek16(0x402 + 2*i);
if (i > 2) x = (x * 1006)/200;
x = (x * 2048)/0x8000;
printf("adc%d=%d\n", i, x);
}
return 0;
}
Running this code on a TS-TPC-8390 with pin 7 of the ADC header (channel 3) connected to 3.3V returns:
root@ts4700:~# ./adctest adc1=0 adc2=0 adc3=3302 adc4=0 adc5=0 adc6=0
| Offset | Bits | Description | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0x0 | 15:8 | Core ID register (reads 0xad) | |||||||||
| 7:6 | Reserved | ||||||||||
| 5:4 |
| ||||||||||
| 3:2 |
| ||||||||||
| 1:0 |
| ||||||||||
| 0x2 | 15:0 | Channel Mask | |||||||||
| 0x4 | 15:0 | Channel 1 most recent conversion value | |||||||||
| 0x6 | 15:0 | Channel 2 most recent conversion value | |||||||||
| 0x8 | 15:0 | Channel 3 most recent conversion value | |||||||||
| 0xa | 15:0 | Channel 4 most recent conversion value | |||||||||
| 0xc | 15:0 | Channel 5 most recent conversion value | |||||||||
| 0xe | 15:0 | Channel 6 most recent conversion value |
The channel mask register controls which channels are enabled. Bits 0-5 enable channels 1-6 respectively. If a given channel is not enabled, (enable bit == 0) it will not be sampled and its conversion value register will contain an obsolete and meaningless value. The more channels that are enabled, the lower the sampling speed on each channel.
Watchdog
By default there is a /dev/watchdog with the tshwctl daemon running at the highest possible priority to feed the watchdog. This is a pipe that is created in userspace, so for many applications this may provide enough functionality for the watchdog by verifying that userspace is still executing applications. If you would like to have the watchdog functionality more tightly integrated with your application you can specify various feed options.
At the lower level there are 3 valid watchdog feed values that are written to the watchdog register in the #Syscon:
| Value | Result |
|---|---|
| 0 | feed watchdog for another .338s |
| 1 | feed watchdog for another 2.706s |
| 2 | feed watchdog for another 10.824s |
| 3 | disable watchdog |
The watchdog is armed by default for 10s for the operating system to take over, after which the startup scripts autofeed the watchdog with:
echo a2 > /dev/watchdog
The /dev/watchdog fifo accepts 3 types of commands:
| Value | Function |
|---|---|
| f<3 digits> | One time feed for a specified amount of time which uses the 3 digit number / 10. For example, "f456" would feed for 45.6 seconds. |
| "0", "1", "2", "3" | One time feed with the value in the above table. |
| a<num 0-3> | This value autofeeds with the value in the above table. |
Most applications should use the f<3 digits> option to more tightly integrate this to their application. For example:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
#include <unistd.h>
void do_some_work(int data) {
/* The contract for sleep(int n) is that it will sleep for at least n
* seconds, but not less. If other kernel threads or processes require
* more time sleep can take longer, but when your process has a high
* priority this is usually measured in millseconds */
sleep(5);
}
int read_some_io() {
/* If this function (or do_some_work) misbehave and stall thee watchdog
* will not be fed in the main loop and cause a reboot. You can test
* this by uncommenting the next line to force an infinite loop */
// while (1) {}
return 42;
}
int main(int argc, char **argv)
{
int wdfd;
/* In languages other than C/C++ this is still essentially the same, but
* make sure you are opening the watchdog file synchronously so the writes
* happen immediately. Many languages will buffer writes together to make
* them more efficient, but the watchdog needs the writes to be timed
* precisely */
wdfd = open("/dev/watchdog", O_SYNC|O_RDWR);
while (1) {
int data;
/* This loop is expected to take about 5-6 seconds, but to allow some
* headroom for other applications, I will feed the watchdog for 10s. */
write(wdfd, "f100", 4);
data = read_some_io();
do_some_work(data);
}
}
MUXBUS
The MUXBUS is the bus between the FPGA on the SoM to communicate with the off-board CPLD. The CPLD controls PC/104 access as well as some DIO. The MUXBUS config register in the Syscon allows enabling and configuring the speed for this bus. The MUXBUS timing also influences the communication with PC/104 peripherals.
For more advanced details on the MUXBUS, refer to the implementation details here.
Most applications can use one of two timing values:
## Fast value (default on TS-8150)
devmem 0x80004004 16 0x181
## Slow value (for older PC104 devices)
# devmem 0x80004004 16 0xf0ff
See the FPGA register layout for where the MUXBUS address space is accessible.
PC/104
The TS-8150 supports 21 bits of PC/104 addressing with the standard 8-bit data as well as our 16-bit data implementation inside the single 104 pin header. Most of the Technologic Systems' simple I/O based PC/104 devices, in either 8 or 16 bit modes, are supported on this platform. Third party 16-bit devices will not be properly supported. But many simple 8-bit PC/104 devices will work without issue.
The PC/104 address space overlays on top of the whole MUXBUS address space. Because of this, addresses 0x00-0xFF are reserved for accessing the PLD. See the table below:
| MUXBUS Address Range | Function |
|---|---|
| 0x0000-0x00FF | TS-8150 register access[1] |
| 0x0100-0x7FFF | PC/104 bus space[2] |
Note that the MUXBUS address space is 15-bit wide (32 KiB) while the TS-8150 PC/104 offers 21 bits of address. Physical PC/104 address bits 20:15 are repeated bits 13:8 of the requested address. The lower 15-bits of address are put on the bus as requested.
See the PC/104 Header section for more information on general PC/104 access
PC/104 ISA16550
You can use the included ts4700_isa16550 driver to load support for various devices such as the TS-IRIDIUM, or TS-MULTI-104.
For example, to load a single device:
# Assumes COM1 and IRQ7 jumpers are set
modprobe ts4700_isa16550 com=0x3f8 irq=7
If you are loading multiple devices, you can specify the COM and IRQ in a single command. For example, to set up a TS-SER4 with only jumpers IRQ4, IRQ2, and COM1 set:
modprobe ts4700_isa16550 irq=6,6,6,6 com=0x3f8,0x2f8,0x3e8,0x2e8
This driver assumes the PC104 base is at 0x0 of the muxbus, but some baseboards such as the TS-8900 use another offset for PC104. This can be specified with the iobase argument:
modprobe ts4700_isa16550 com=0x3f8 irq=7 iobase=0x81008800
XUARTS
The XUARTs are ttl serial ports implemented in the FPGA. These communicate with the userspace driver xuartctl. Each XUART core in the FPGA can handle up to 8 XUARTs, though the default TS-4710 FPGA contains 6. The XUART serial ports have a single shared 4kByte receive FIFO which makes real time interrupt latency response less of a concern and in actual implementation, the serial ports are simply polled at 100Hz and don't even use an IRQ. Even with all 8 ports running at 230400 baud, it is not possible to overflow the receive FIFO in 1/100th of a second. The "xuartctl --server" daemon is started by default in the init scripts which sets up listening TCP/IP ports for all XUART channels on ports 7350-7357. An application may simply connect to these ports via localhost (or via the network) and use the serial ports as if they were network services.
The typical method for accessing xuarts is using the pts layer. For example:
eval $(xuartctl --server --port 3 --mode=8n1 --speed 9600 2>&1); ln -s $ttyname /dev/ttyxuart3
This will set up XUART port 3 to 9600 baud, 8n1, and symlink it to /dev/ttyxuart3. In your application you can open the /dev/ttyxuart3 and for most part you can access this just like any other uart. When using the PTS layer, there are several operations that are not supported. The mode and baud rate must be set up with xuartctl, and cannot be programatically changed with the standard ioctl.
The XUARTs can be managed with xuartctl. See the xuartctl page for more details on programming with XUARTs. See either of these links for more information on using serial ports in Linux:
CAN
The CAN controller contained in the FPGA is compatible with the register interface for the SJA1000. This is implemented using SocketCAN.
Before proceeding with the examples, see the Kernel's CAN documentation here.
This board comes preinstalled with can-utils which can be used to communicate over a CAN network without writing any code. The candump utility can be used to dump all data on the network
## First, set the baud rate and bring up the device:
ip link set can0 type can bitrate 250000
ip link set can0 up
## Dump data & errors:
candump -cae can0,0:0,#FFFFFFFF &
## Send the packet with:
#can_id = 0x7df
#data 0 = 0x3
#data 1 = 0x1
#data 2 = 0x0c
cansend can0 7Df#03010c
This example packet is designed to work with the Ozen Elektronik myOByDic 1610 ECU simulator to read the RPM speed. This device will return data from candump with:
can0 7DF [3] 03 01 0C '...' can0 7E8 [8] 04 41 0C 2F C0 00 00 00 '.A./....' can0 7E9 [8] 04 41 0C 2F 80 00 00 00 '.A./....'
In this case, 0x2f is the current RPM value. This shows a simple way you can prove out the communication before moving to another language, but this next example sends the same packet and parses the same response in C:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <pthread.h>
#include <net/if.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <net/if.h>
#include <sys/ioctl.h>
#include <assert.h>
#include <linux/can.h>
#include <linux/can/raw.h>
int main(void)
{
int s;
int nbytes;
struct sockaddr_can addr;
struct can_frame frame;
struct ifreq ifr;
struct iovec iov;
struct msghdr msg;
char ctrlmsg[CMSG_SPACE(sizeof(struct timeval)) + CMSG_SPACE(sizeof(__u32))];
char *ifname = "can0";
if((s = socket(PF_CAN, SOCK_RAW, CAN_RAW)) < 0) {
perror("Error while opening socket");
return -1;
}
strcpy(ifr.ifr_name, ifname);
ioctl(s, SIOCGIFINDEX, &ifr);
addr.can_family = AF_CAN;
addr.can_ifindex = ifr.ifr_ifindex;
if(bind(s, (struct sockaddr *)&addr, sizeof(addr)) < 0) {
perror("socket");
return -2;
}
/* For the ozen myOByDic 1610 this requests the RPM guage */
frame.can_id = 0x7df;
frame.can_dlc = 3;
frame.data[0] = 3;
frame.data[1] = 1;
frame.data[2] = 0x0c;
nbytes = write(s, &frame, sizeof(struct can_frame));
if(nbytes < 0) {
perror("write");
return -3;
}
iov.iov_base = &frame;
msg.msg_name = &addr;
msg.msg_iov = &iov;
msg.msg_iovlen = 1;
msg.msg_control = &ctrlmsg;
iov.iov_len = sizeof(frame);
msg.msg_namelen = sizeof(struct sockaddr_can);
msg.msg_controllen = sizeof(ctrlmsg);
msg.msg_flags = 0;
do {
nbytes = recvmsg(s, &msg, 0);
if (nbytes < 0) {
perror("read");
return -4;
}
if (nbytes < (int)sizeof(struct can_frame)) {
fprintf(stderr, "read: incomplete CAN frame\n");
}
} while(nbytes == 0);
if(frame.data[0] == 0x4)
printf("RPM at %d of 255\n", frame.data[3]);
return 0;
}
Other languages have bindings to access CAN such as Python using C-types, Java using JNI.
Baseboard Register Map
All of these registers are intended for 16 bit access. You can find this range at 0x80008000. The MUXBUS configuration register must first be set before accessing this range. For example, to read the board ID:
devmem 0x80008000 16 # Read Board ID register (0x0)
| Offset | Bits | Access | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0x0 | 15:0 | Read Only | Board ID (0x8150) |
| 0x2 | 3:0 | Read Only | PLD revision |
| 7:4 | Read/Write | Value to control PWM for LCD contrast | |
| 8 | Read/Write | TS-8150 USB Reset | |
| 9 | Read/Write | Controls ISA_RESET on the PC/104 bus | |
| 10 | Read/Write | Enables a 14.3 MHz clock on the PC/104 bus (B30) and the PLD (default 1) | |
| 11 | Read/Write | Enables the RS-232 transceiver (default 1) | |
| 12 | Read/Write | Toggles 5 V to the LCD header pin 1 | |
| 13 | Read/Write | Enable CAN1 standby | |
| 14 | Read/Write | Enable CAN2 standby | |
| 15 | Read/Write | Enables the PWM output for the contrast value | |
| 0x4 | 1:0 | Read/Write | PC/104 B12:B11 output data |
| 2 | Read/Write | PC/104 B19 output data | |
| 15:3 | N/A | Reserved | |
| 0x6 | 7:0 | Read/Write | LCD pins 14:7 output data |
| 8 | Read/Write | LCD Header pin 6 output data | |
| 9 | Read/Write | LCD Header pin 3 output data | |
| 10 | Read/Write | LCD Header pin 5 output data | |
| 11 | Read/Write | AVR MOSI | |
| 12 | Read/Write | AVR SCLK | |
| 13 | Read/Write | AVR RESET | |
| 14:15 | N/A | Reserved | |
| 0x8 | 1:0 | Read/Write | PC/104 B12:B11 data direction |
| 2 | Read/Write | PC/104 B19 data direction | |
| 15:3 | N/A | Reserved | |
| 0xa | 7:0 | Read/Write | LCD pins 14:7 data direction |
| 8 | Read/Write | LCD Header pin 6 data direction | |
| 9 | Read/Write | LCD Header pin 3 data direction | |
| 10 | Read/Write | LCD Header pin 5 data direction | |
| 15:11 | N/A | Reserved | |
| 0xc | 1:0 | Read Only | PC/104 B12:B11 input |
| 2 | Read Only | PC/104 B19 input data | |
| 15:3 | N/A | Reserved | |
| 0xe | 7:0 | Read Only | LCD header pins 14-7 input data |
| 8 | Read Only | LCD Write/Read (pin 6) input data | |
| 9 | Read Only | LCD Register Select (pin 3) input data | |
| 10 | Read Only | LCD Enable (pin 5) input data | |
| 11 | Read/Write | AVR MISO | |
| 15:12 | N/A | Reserved |
| Note: | The registers for controlling the #DIO Header are not used on the TS-8150. On the TS-8150 these are brought from the FPGA on the SoM. Refer to the #DIO Header section for more details. |
External Interfaces
Jumpers
The TS-8150 includes a header with several jumpers and signals:
|
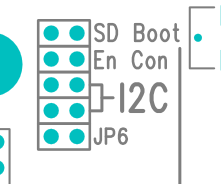
|
You can read JP6 with:
echo $(($(devmem 0xd4019004 32) >> 10 & 0x1))
This will return 0 when the jumper is on, and 1 when the jumper is off.
USB Port
The USB is available on two ports as a USB 2.0 host.
 |
|
| Note: | The TS-4710 OTG port (bottom USB) does not support automatic enumeration when hotplugging devices. Refer to the #USB OTG section for more details. |
DIO header
The TS-8100 includes a 2x8 0.1" pitch header with 8 DIO, I2C, and SPI. Most DIO on this header are rated for 3.3V and are not tolerant of 5V IO. The only exception is SPI_MOSI which is 5V tolerant. The DIO on this baseboard can be accessed by manipulating the TS-8100 Register Map.
All DIO pins on this header have 3.9K pull up resistors.
| Pinout | Header | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
This header is designed to connect to the KPAD accessory which uses the odd DIO on this header to scan a 4x4 keypad. This example scans the KPAD and prints out the pressed character.
/* KPAD 4x4 keypad example code
*
* To compile, copy to the board and run:
* gcc kpad.c -o kpad */
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdint.h>
#include <sys/mman.h>
#include <sys/stat.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
#include <unistd.h>
volatile uint16_t *syscon = 0;
// Map DIO 14,13,11,10,8,7,6,4 to "out" as bits 0:7
const int pins[8] = {14,13,11,10,8,7,6,4};
uint16_t peek16(uint16_t addr)
{
uint16_t value;
if(syscon == 0) {
int mem = open("/dev/mem", O_RDWR|O_SYNC);
syscon = mmap(0,
getpagesize(),
PROT_READ|PROT_WRITE,
MAP_SHARED,
mem,
0x80004000);
}
return syscon[addr/2];
}
void poke16(uint16_t addr, uint16_t value)
{
if(syscon == 0) {
int mem = open("/dev/mem", O_RDWR|O_SYNC);
syscon = mmap(0,
getpagesize(),
PROT_READ|PROT_WRITE,
MAP_SHARED,
mem,
0x80004000);
}
syscon[addr/2] = value;
}
void set_output(uint8_t out)
{
uint16_t val = peek16(0x10);
int i;
for (i = 0; i < 8; i++)
{
if(out & (1 << i)) val |= (1 << pins[i]);
else val &= ~(1 << pins[i]);
}
poke16(0x10, val);
}
void set_ddr(uint8_t ddr)
{
uint16_t val = peek16(0x18);
int i;
for (i = 0; i < 8; i++)
{
if(ddr & (1 << i)) val |= (1 << pins[i]);
else val &= ~(1 << pins[i]);
}
poke16(0x18, val);
}
uint8_t get_input()
{
uint16_t val = peek16(0x20);
uint8_t in = 0;
int i;
for (i = 0; i < 8; i++)
{
if(val & (1 << pins[i])) in |= (1 << i);
else in &= ~(1 << i);
}
return in;
}
int main()
{
uint8_t ddr = 0x0f;
uint8_t out = 0xff;
int row, col;
char *keys[4][4] = {
{ "1", "2", "3", "UP" },
{ "4", "5", "6", "DOWN" },
{ "7", "8", "9", "2ND" },
{ "CLEAR", "0", "HELP", "ENTER" }
};
//set first 4 as outputs, last 4 as inputs
set_ddr(ddr);
while(1) {
for(row = 0; row < 4; row++) {
set_output(~(1 << row));
usleep(50000);
uint16_t in = get_input();
for(col = 4; col < 8; col++) {
if(~in & (1 << col)) {
// If we read it, sleep and read again to debounce
usleep(1000);
in = get_input();
if(~in & (1 << col)) {
printf("%s\n", keys[row][col - 4]);
fflush(stdout);
}
}
}
}
}
return 0;
}
LCD Header
The LCD header is designed around compatibility with our low cost LCD-LED: Alphanumeric 2x24 LCD. These IO are accessed through manipulation of the registers directly. Connector CN8 is a 14 pin (2x7) 0.1" spacing header.
| Pinout | Header | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
- ↑ Provides up to 1400mA
| WARNING: | LCD_D0 thru LCD_D7 are 5V tolerant. LCD_WR#, LCD_RS, and LCD_EN are not. |
This example project allows you to pipe in data separated by newlines, or you can call the application with arguments to draw the two lines. For example:
./lcd Technologic Systems
Will write this to the screen:

|
/* LCD 2x24 character example code
*
* To compile, copy to the board and run:
* gcc lcd.c -o lcd */
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdint.h>
#include <sys/mman.h>
#include <sys/stat.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <time.h>
void lcd_init(void);
void lcd_wait(void);
void lcd_command(unsigned int cmd);
void lcd_writechars(unsigned char *dat);
// These are nanosecond delays
#define SETUP 800
#define PULSE 1600
#define HOLD 800
// The mpeek/mpoke functions are specific to the TS-47XX
volatile uint16_t *muxbus = 0;
int mem = 0;
uint16_t mpeek16(uint16_t addr)
{
uint16_t value;
if (mem == 0)
mem = open("/dev/mem", O_RDWR|O_SYNC);
if(muxbus == 0)
muxbus = mmap(0,
getpagesize(),
PROT_READ|PROT_WRITE,
MAP_SHARED,
mem,
0x80008000);
return muxbus[addr/2];
}
void mpoke16(uint16_t addr, uint16_t value)
{
if (mem == 0)
mem = open("/dev/mem", O_RDWR|O_SYNC);
if(muxbus == 0)
muxbus = mmap(0,
getpagesize(),
PROT_READ|PROT_WRITE,
MAP_SHARED,
mem,
0x80008000);
muxbus[addr/2] = value;
}
void lcd_init(void) {
uint16_t out;
// Data lines to inputs, control lines to outputs
mpoke16(0xa, 0x700);
out = mpeek16(0x6);
// Set LCD_EN and LCD_RS low
out &= ~(0x600);
// Set LCD_WR high
out |= 0x100;
mpoke16(0x6, out);
usleep(15000);
lcd_command(0x38); // two rows, 5x7, 8 bit
usleep(4100);
lcd_command(0x38); // two rows, 5x7, 8 bit
usleep(100);
lcd_command(0x38); // two rows, 5x7, 8 bit
lcd_command(0x6); // cursor increment mode
lcd_wait();
lcd_command(0x1); // clear display
lcd_wait();
lcd_command(0xc); // display on, blink off, cursor off
lcd_wait();
lcd_command(0x2); // return home
}
void lcd_wait(void) {
uint16_t ddr, out, in;
int i, dat, tries = 0;
struct timespec dly;
dly.tv_sec = 0;
mpoke16(0xa, mpeek16(0xa) & 0xff00);
out = mpeek16(0x6);
do {
// step 1, apply RS & WR
out |= 0x100; // de-assert WR
out &= ~0x200; // de-assert RS
mpoke16(0x6, out);
// step 2, wait
dly.tv_nsec = SETUP;
nanosleep(&dly, NULL);
// step 3, assert EN
out |= 0x400;
mpoke16(0x6, out);
// step 4, wait
dly.tv_nsec = PULSE;
nanosleep(&dly, NULL);
// step 5, de-assert EN, read result
in = mpeek16(0xe) & 0xff;
out &= ~0x400; // de-assert EN
mpoke16(0x6, out);
// step 6, wait
dly.tv_nsec = HOLD;
nanosleep(&dly, NULL);
} while (in & 0x80 && tries++ < 1000);
}
void lcd_command(unsigned int cmd) {
int i;
uint16_t out;
struct timespec dly;
dly.tv_sec = 0;
// Set port A to outputs
mpoke16(0xa, mpeek16(0xa) | 0x00ff);
out = mpeek16(0x6);
// step 1, apply RS & WR, send data
out &= 0xff00;
out |= (cmd & 0xff);
out &= ~(0x300); // de-assert RS, assert WR
mpoke16(0x6, out);
// step 2, wait
dly.tv_nsec = SETUP;
nanosleep(&dly, NULL);
// step 3, assert EN
out |= 0x400;
mpoke16(0x6, out);
// step 4, wait
dly.tv_nsec = PULSE;
nanosleep(&dly, NULL);
// step 5, de-assert EN
out &= ~0x400;
mpoke16(0x6, out);
// step 6, wait
dly.tv_nsec = HOLD;
nanosleep(&dly, NULL);
}
void lcd_writechars(unsigned char *dat) {
int i;
uint16_t out = mpeek16(0x6);
struct timespec dly;
dly.tv_sec = 0;
do {
lcd_wait();
// set data lines to outputs
mpoke16(0xa, mpeek16(0xa) | 0x00ff);
// step 1, apply RS & WR, send data
out &= 0xff00;
out |= *dat++;
out |= 0x200; // assert RS
out &= ~0x100; // assert WR
mpoke16(0x6, out);
// step 2
dly.tv_nsec = SETUP;
nanosleep(&dly, NULL);
// step 3, assert EN
out |= 0x400;
mpoke16(0x6, out);
// step 4, wait 800 nS
dly.tv_nsec = PULSE;
nanosleep(&dly, NULL);
// step 5, de-assert EN
out &= ~0x400;
mpoke16(0x6, out);
// step 6, wait
dly.tv_nsec = HOLD;
nanosleep(&dly, NULL);
} while(*dat);
}
/* This program takes lines from stdin and prints them to the
* 2 line LCD connected to the TS-8100/TS-8160 LCD header. e.g
*
* echo "hello world" | lcdmesg
*
* It may need to be tweaked for different size displays
*/
int main(int argc, char **argv)
{
int i = 0;
lcd_init();
if (argc == 2) {
lcd_writechars(argv[1]);
}
if (argc > 2) {
lcd_writechars(argv[1]);
lcd_wait();
lcd_command(0xa8); // set DDRAM addr to second row
lcd_writechars(argv[2]);
}
if (argc >= 2) return 0;
while(!feof(stdin)) {
unsigned char buf[512];
lcd_wait();
if (i) {
// XXX: this seek addr may be different for different
// LCD sizes! -JO
lcd_command(0xa8); // set DDRAM addr to second row
} else {
lcd_command(0x2); // return home
}
i = i ^ 0x1;
if (fgets(buf, sizeof(buf), stdin) != NULL) {
unsigned int len;
buf[0x27] = 0;
len = strlen(buf);
if (buf[len - 1] == '\n') buf[len - 1] = 0;
lcd_writechars(buf);
}
}
return 0;
}
COM Headers
PC/104 Header
See the #MUXBUS section for more details on working with the MUXBUS peripherals.
The PC/104 connector consists of two rows of pins labeled A and B, the numbering of which is shown below. The signals for the PC/104 interface are generated by a MAX240 PLD on the TS-8150. It converts the MUXBUS cycles from the SoM to PC/104 bus cycles and provides some GPIO pins for finer control of the PC/104 interface.
Any of the I/O labeled DIO_* can be controlled through manipulation of the TS-8150 registers directly. See the PC/104 interface section for more information on how the pins are driven.
|
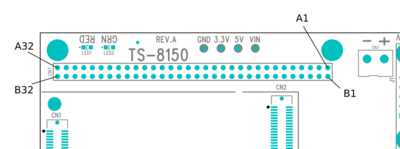
|
| WARNING: | Most of the pins on the PC104 bus are 3.3 V tolerant. Refer to the schematic for more details. |
Revisions and Changes
TS-4712 PCB Revisions
| Revision | Changes |
|---|---|
| A |
|
TS-8150 PCB Revisions
| PCB Revision | Description |
|---|---|
| A | Initial release |
FPGA Changelog
| Revision | Changes |
|---|---|
| 5 |
|
| 4 |
|
| 3 |
|
| 2 |
|
| 1 | Enabled XUARTs and CAN |
| 0 | Initial release |
You can update to the latest FPGA by booting to Debian and running:
cd /ts/
wget ftp://ftp.embeddedTS.com/ts-socket-macrocontrollers/ts-4710-linux/binaries/ts-bitstreams/ts4710-fpga-latest.vme.bz2
# The TS-4710 and TS-4712 use the same FPGA. This will
# move it to the correct name for either.
mv ts4710-fpga-latest.vme.bz2 ts$(cat /dev/tsmodel)-fpga.vme.bz2
The FPGA is loaded in to the FPGA SRAM on every load, so this file will need to exist for all future boots.
Software Images
2.6 Debian Changelog
This is the changelog for the software image which is shared from the TS-4710, TS-4712, TS-4720, TS-4740, TS-7700, and the TS-7250-V2.
| Image File | Changelog | Known Issues |
|---|---|---|
| 2gbsd-471x-20130221.dd.bz2 |
|
|
| 2gbsd-471x-20130221.dd.bz2 |
|
|
| 2gbsd-471x-20130515.dd.bz2 |
|
|
| 2gbsd-471x-20130522.dd.bz2 |
|
|
| 2gbsd-471x-20130531.dd.bz2 |
|
|
| 2gbsd-471x-20130806.dd.bz2 |
|
|
| 2gbsd-471x-20130815.dd.bz2 |
|
|
| 4gbsd-471x-20131004.dd.bz2 |
|
|
| 4gbsd-471x-20140306.dd.bz2 |
|
|
| 4gbsd-471x-20140430.dd.bz2 |
|
|
| * 4gbsd-471x-20140724.dd.bz2 |
|
* EVGPIO IRQ #2 requires a build from the latest kernel sources |
| * 4gbsd-471x-20140924.dd.bz2 |
|
|
| * 4gbsd-471x-20141013.dd.bz2 |
|
|
|
||
|
||
|
3.14 Debian Changelog
| Image File | Changelog | Known Issues | |
|---|---|---|---|
| * 4gbsd-471x-3x-20140828.dd.bz2 |
|
| |
|
| ||
|
| ||
|
| ||
|
Further Resources
For further support you can go to our Developer Forums here. You can also contact us for more information.
We recommend reading our white papers if they are relevant to your project:
For learning more about Debian:
- The Debian Handbook (online or book)
- Learning Debian GNU/Linux (book)
- Debian Administration (online)
For Linux programming in general:
- The Linux Documentation Project (online)
- The Linux Programming Interface (book)
- Linux System Programming (book)
- Linux in a Nutshell (book)
Product Notes
FCC Advisory
This equipment generates, uses, and can radiate radio frequency energy and if not installed and used properly (that is, in strict accordance with the manufacturer's instructions), may cause interference to radio and television reception. It has been type tested and found to comply with the limits for a Class A digital device in accordance with the specifications in Part 15 of FCC Rules, which are designed to provide reasonable protection against such interference when operated in a commercial environment. Operation of this equipment in a residential area is likely to cause interference, in which case the owner will be required to correct the interference at his own expense.
If this equipment does cause interference, which can be determined by turning the unit on and off, the user is encouraged to try the following measures to correct the interference:
Reorient the receiving antenna. Relocate the unit with respect to the receiver. Plug the unit into a different outlet so that the unit and receiver are on different branch circuits. Ensure that mounting screws and connector attachment screws are tightly secured. Ensure that good quality, shielded, and grounded cables are used for all data communications. If necessary, the user should consult the dealer or an experienced radio/television technician for additional suggestions. The following booklets prepared by the Federal Communications Commission (FCC) may also prove helpful:
How to Identify and Resolve Radio-TV Interference Problems (Stock No. 004-000-000345-4) Interface Handbook (Stock No. 004-000-004505-7) These booklets may be purchased from the Superintendent of Documents, U.S. Government Printing Office, Washington, DC 20402.
Limited Warranty
See our Terms and Conditions for more details.